RF Flip Chip Package Substrate Manufacturer
RF Flip Chip Package Substrate Manufacturer,RF Flip Chip Package Substrates are advanced components crucial for high-frequency RF applications. They utilize flip chip technology to mount ICs directly onto substrates, minimizing signal loss and enhancing performance. Made from materials like high-frequency laminates or ceramics, these substrates ensure optimal signal integrity, thermal management, and reliability in telecommunications, aerospace, and consumer electronics. Their design focuses on controlled impedance, precise routing of RF traces, and effective thermal dissipation, making them essential for applications requiring high-speed data transmission and wireless communication. RF flip chip package substrates play a vital role in achieving superior RF system performance and functionality.
What is an RF Flip Chip Package Substrate?
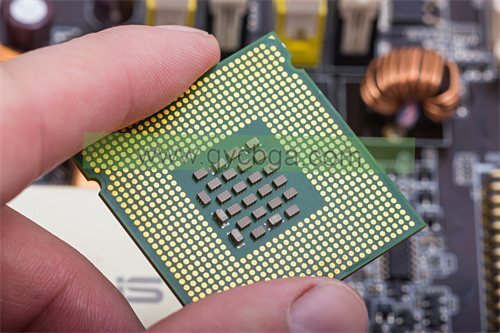
An RF flip chip package substrate is a specialized component used in semiconductor packaging, particularly for radio frequency (RF) applications. It serves as a platform to mount and connect integrated circuits (ICs) using flip chip technology, which involves flipping the IC upside down and directly bonding its contact pads to corresponding pads on the substrate. This method offers advantages such as shorter signal paths, reduced inductance, and improved high-frequency performance compared to traditional wire bonding.
The substrate itself is a crucial part of the RF flip chip package, designed to provide electrical interconnections between the IC and other components like antennas or transmission lines. It is engineered with materials that minimize signal loss and interference at high frequencies, often using specialized dielectric materials and metal traces optimized for RF signals.
Key features of an RF flip chip package substrate include precise alignment and bonding of the IC, thermal management to dissipate heat generated by the IC, and compatibility with RF transmission requirements such as impedance matching and signal integrity. These substrates are essential in applications demanding high-speed data transmission, wireless communication, radar systems, and other RF-intensive technologies where performance and reliability are critical.
RF Flip Chip Package Substrate Manufacturer
What are the RF Flip Chip Package Substrate Design Guidelines?
Design guidelines for RF flip chip package substrates are critical to ensure optimal performance in high-frequency applications. Here are some key guidelines:
- Material Selection:Choose substrate materials with low dielectric constant (εr) and low dissipation factor (tan δ) to minimize signal loss and maintain signal integrity at high frequencies. Materials like high-frequency laminates (e.g., PTFE-based materials like Rogers RO4000 series) are commonly used.
- Layer Stackup Design: Design the substrate with a controlled impedance stackup that matches the impedance of the RF traces (typically 50 ohms for RF applications). This helps in minimizing signal reflections and ensuring efficient signal transmission.
- RF Trace Routing:Route RF signal traces carefully to maintain controlled impedance throughout the signal path. Use wide traces to reduce resistance and inductance, and minimize vias to avoid additional impedance changes and signal losses.
- Grounding Strategy: Implement a solid ground plane beneath the RF signal traces to provide a low-inductance return path. This helps in reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk.
- Via Design: If vias are necessary, use through-hole vias with a sufficient diameter to minimize impedance discontinuities. Consider using via fences or stitching vias around critical RF signal paths to improve grounding and reduce electromagnetic interference.
- Component Placement: Place RF components and flip chip ICs to minimize signal path lengths and reduce parasitic capacitance and inductance. Consider the proximity of components to optimize RF signal routing.
- Thermal Management: Ensure adequate thermal vias and thermal pads to efficiently dissipate heat from the flip chip ICs. Thermal management is crucial to maintaining long-term reliability and preventing thermal-induced performance degradation.
- Manufacturing Tolerances: Design with manufacturing tolerances in mind to ensure consistency and reliability in mass production. Consider the capabilities and limitations of the chosen substrate fabrication process.
- EMI Shielding: Incorporate EMI shielding techniques such as RF shielding cans or conductive coatings where necessary to minimize electromagnetic interference and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
- Simulation and Testing: Validate the substrate design using electromagnetic simulation tools to predict and optimize RF performance. Perform prototype testing to verify design parameters such as impedance matching, insertion loss, and return loss.
By adhering to these design guidelines, engineers can effectively optimize RF flip chip package substrates for high-frequency applications, ensuring robust performance and reliability in demanding RF environments.
What is the RF Flip Chip Package Substrate Fabrication Process?
The fabrication process of an RF flip chip package substrate involves several key steps to ensure the substrate meets the stringent requirements for high-frequency applications. Here’s a general overview of the process:
- Material Selection: Choose appropriate substrate materials with low dielectric constant (εr) and low dissipation factor (tan δ) suitable for RF applications. Common materials include high-frequency laminates such as PTFE-based materials (e.g., Rogers RO4000 series) or ceramic substrates (e.g., alumina or aluminum nitride).
- Layer Preparation:Begin with preparing the substrate layers. This involves cutting the substrate material into appropriate sizes and preparing the surfaces for subsequent processing steps.
- Cleaning and Surface Preparation: Clean the substrate surfaces thoroughly to remove contaminants that could affect bonding and performance. Surface preparation may also involve treatments to enhance adhesion.
- Multilayer Lamination: If the substrate is multilayered, perform lamination by stacking and bonding individual layers together. This process uses heat and pressure to bond the layers and ensure a strong, reliable substrate structure.
- Drilling: Drill holes for vias and through-holes as required by the substrate design. Precision drilling ensures accurate placement and size of holes, which are crucial for vias and component mounting.
- Copper Plating: Plate the substrate with copper to form conductive traces and pads. This process includes depositing a thin layer of copper onto the substrate surface using techniques such as electroplating or sputtering.
- Circuit Patterning: Use photolithography and etching techniques to define the circuit patterns on the substrate. A photoresist is applied and exposed to UV light through a photomask, followed by chemical etching to remove unwanted copper and define the conductive traces.
- Surface Finish: Apply a suitable surface finish to the substrate to protect the copper traces and ensure good solderability. Common surface finishes include immersion gold (ENIG), immersion silver, or OSP (Organic Solderability Preservatives).
- Component Attachment: If flip chip technology is used, prepare the substrate for flip chip attachment. This involves ensuring the substrate has appropriate pads and solder bumps for flip chip bonding.
- Quality Control and Testing: Throughout the fabrication process, perform quality control checks and inspections to ensure the substrate meets design specifications. Test the finished substrates for parameters such as dimensional accuracy, electrical continuity, impedance matching, and reliability.
- Packaging and Delivery: Finally, package the substrates appropriately for protection during transportation and storage. Ensure proper documentation and traceability of substrates for quality assurance purposes.
The RF flip chip package substrate fabrication process requires precision and adherence to design specifications to achieve optimal performance in high-frequency applications. Advanced manufacturing techniques and quality assurance practices are essential to produce substrates capable of meeting the stringent requirements of RF circuits and systems.
How do you manufacture an RF Flip Chip Package Substrate?
Manufacturing an RF flip chip package substrate involves a series of intricate steps to ensure high performance and reliability in RF applications. Here’s an expanded overview of the process:
- Material Selection: Choose substrate materials based on their electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties suitable for RF frequencies. High-frequency laminates like PTFE-based materials (e.g., Rogers RO4000 series) or ceramic substrates (e.g., alumina or aluminum nitride) are commonly used due to their low dielectric constant (εr) and low dissipation factor (tan δ).
- Substrate Preparation: Begin by preparing the substrate material into the required dimensions. This may involve cutting, cleaning, and surface treatment to remove contaminants and prepare the surface for subsequent processing.
- Layer Stacking and Lamination: If the substrate is multilayered, stack the individual layers together. The layers are then laminated under heat and pressure to bond them into a single substrate structure. This step ensures mechanical stability and uniformity across the substrate.
- Drilling: Precision drilling is performed to create holes for vias and through-holes. Vias are crucial for creating electrical connections between different layers and components on the substrate. The size, placement, and density of vias are critical factors in maintaining signal integrity and impedance control in RF circuits.
- Copper Deposition: Coat the substrate with copper through a process like electroplating or sputtering. This forms the conductive traces and pads required for electrical connections on the substrate. The thickness and quality of the copper layer are controlled to meet design specifications for electrical performance.
- Circuit Patterning: Use photolithography to define the circuit patterns on the substrate. A photoresist is applied and exposed to UV light through a photomask, which defines the desired conductive trace patterns. Chemical etching removes unwanted copper, leaving behind the designed traces and pads on the substrate.
- Surface Finishing: Apply a suitable surface finish to the substrate to protect the copper traces and ensure good solderability. Common surface finishes include immersion gold (ENIG), immersion silver, or OSP (Organic Solderability Preservatives). The choice of surface finish depends on factors like environmental conditions and soldering processes used in assembly.
- Component Attachment: Prepare the substrate for flip chip attachment if flip chip technology is employed. This involves creating pads and applying solder bumps or conductive adhesives on the substrate surface. Flip chip bonding involves placing the IC upside down (flip chip) and bonding its contact pads directly to corresponding pads on the substrate using solder reflow or conductive adhesives.
- Quality Assurance: Throughout the manufacturing process, conduct rigorous quality control checks and inspections. Test the substrates for dimensional accuracy, electrical continuity, impedance matching, and reliability. Advanced techniques such as X-ray inspection and automated optical inspection (AOI) may be employed to detect defects and ensure high yield and reliability.
- Packaging and Delivery:Once manufactured and tested, package the substrates securely for transportation and storage. Proper labeling and documentation ensure traceability and compliance with customer requirements and industry standards.
Manufacturing RF flip chip package substrates demands precision in material selection, process control, and quality assurance to meet the stringent performance requirements of high-frequency RF applications. Advanced manufacturing technologies and continuous improvement in process capabilities are essential to produce substrates capable of delivering reliable performance in complex RF circuits and systems.
How much should an RF Flip Chip Package Substrate cost?
The cost of an RF flip chip package substrate can vary widely depending on several factors:
- Material: The type of substrate material used (e.g., high-frequency laminates, ceramic substrates) significantly impacts the cost. High-performance materials like PTFE-based laminates or specialized ceramics tend to be more expensive than standard FR-4 materials due to their superior electrical properties.
- Complexity: The complexity of the substrate design, including the number of layers, density of vias, and complexity of circuit patterns, influences manufacturing costs. Multilayer substrates with fine-pitch traces and high-density vias require more sophisticated manufacturing processes and may incur higher costs.
- Size and Quantity: Larger substrates or orders in higher quantities generally reduce per-unit costs due to economies of scale in manufacturing and materials procurement.
- Surface Finish: The choice of surface finish (e.g., immersion gold, OSP) affects costs. Some finishes may require additional processing steps or higher-quality materials, impacting overall substrate cost.
- Quality Standards: Substrates manufactured to meet stringent quality standards, such as those required for aerospace, defense, or high-reliability applications, may incur higher costs due to additional testing and quality assurance measures.
- Supplier and Location: Costs can vary between suppliers and geographic regions based on factors like labor costs, overheads, and local market conditions.
To provide a ballpark figure, the cost of a basic RF flip chip package substrate for moderate RF frequencies and standard applications could range from a few dollars to tens of dollars per substrate. For substrates used in high-frequency RF applications or requiring specialized materials and processes, costs can be higher, potentially ranging into the hundreds of dollars per substrate.
For accurate pricing, it’s advisable to consult with substrate manufacturers or suppliers who can provide quotes based on specific design requirements, material choices, and volume considerations. They can also offer insights into optimizing substrate designs to balance performance requirements with cost-effectiveness.
What is RF Flip Chip Package Substrate base material?
The base material used for RF flip chip package substrates typically depends on the specific requirements of the RF application. Here are two common types of materials used:
- High-Frequency Laminates: These are engineered materials designed specifically for high-frequency RF applications. They typically consist of a laminate construction with a core material and copper foil layers. The core material is often based on PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) or PTFE composite materials, which have a low dielectric constant (εr) and low dissipation factor (tan δ). Examples include the Rogers RO4000 series (RO4350B, RO4003C) and Taconic TLY series. These laminates offer excellent electrical properties, such as low loss tangent and stable dielectric constant across a wide frequency range, making them ideal for high-frequency RF circuits.
- Ceramic Substrates: For even higher frequencies and power handling capabilities, ceramic substrates such as alumina (Al2O3) or aluminum nitride (AlN) are used. These substrates have excellent thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and stability over a wide temperature range. They are suitable for applications requiring high power density and low signal loss, such as in microwave and millimeter-wave RF circuits. Ceramic substrates are often used in conjunction with thick film or thin film metallization techniques to create the necessary circuit patterns and interconnections.
In both cases, the choice of base material is critical to achieving desired electrical performance characteristics such as controlled impedance, low insertion loss, and minimal signal distortion. The substrate material must also exhibit good thermal management properties to dissipate heat generated by RF components effectively.
Manufacturers select the base material based on factors such as frequency of operation, power handling requirements, thermal management needs, and overall performance specifications dictated by the RF design. Each material type has its advantages and trade-offs, allowing engineers to tailor the substrate to meet the specific demands of their RF application.
Which company makes RF Flip Chip Package Substrates?
RF Flip Chip Package Substrates are specialized substrates used in high-frequency RF applications. Common manufacturers include Rogers Corporation from the United States, Mitsui Chemicals from Japan, and Deltamicros from Germany. These companies leverage their expertise in high-frequency electronic materials and packaging technologies to provide a variety of substrate materials and solutions tailored for RF packaging.
At our company, we also possess the capability and experience to manufacture RF Flip Chip Package Substrates. We utilize advanced manufacturing technologies and stringent quality control processes to produce high-performance substrates that meet the requirements of high-frequency applications. Here are some of the advantages and capabilities we offer:
- Material Selection and Process Control: We can select suitable substrate materials such as high-frequency laminates (e.g., Rogers RO4000 series), ceramic substrates, etc., according to customer specifications to ensure excellent electrical and thermal properties.
- Multilayer Substrate Design and Manufacturing: We have the capability to design and manufacture multilayer substrates, supporting complex circuit layouts and high-density interconnect requirements.
- Precision Machining and Reliability Assurance: Our manufacturing equipment and processes enable precise drilling, circuit pattern definition, and surface treatment, ensuring dimensional accuracy and electrical performance as per design requirements.
- Quality Control and Testing: We implement rigorous quality control measures, conducting thorough inspections and tests at every production stage to ensure the stability and reliability of substrates.
- Customization and Technical Support: We provide customized design and manufacturing services tailored to specific application requirements. Additionally, our team offers professional technical support and advice to help customers achieve their performance goals in the RF domain.
As a company with extensive experience and technical expertise, we are committed to producing high-quality RF Flip Chip Package Substrates that provide reliable support for customers’ high-frequency RF electronic products. We continuously strive to enhance our technological capabilities and production efficiency to meet various challenges and requirements in RF packaging.
What are the 7 qualities of good customer service?
Good customer service is characterized by several key qualities that contribute to a positive and satisfying experience for customers. Here are seven important qualities:
- Responsiveness: Being prompt and timely in addressing customer inquiries, concerns, and requests. This includes acknowledging customer communications quickly and providing timely solutions or assistance.
- Empathy: Understanding and empathizing with the customer’s situation, emotions, and needs. It involves actively listening to customers, showing genuine concern, and demonstrating empathy in interactions.
- Patience: Maintaining composure and patience, especially when dealing with challenging or frustrated customers. Patience allows service representatives to handle situations calmly, listen attentively, and work towards resolving issues effectively.
- Knowledgeability: Possessing sufficient knowledge and expertise about products or services offered. This enables service representatives to provide accurate information, answer questions confidently, and offer relevant solutions or recommendations.
- Clarity: Communicating clearly and effectively with customers. This involves using language that is easy to understand, providing clear instructions or explanations, and avoiding jargon or technical terms unless appropriate.
- Professionalism:Conducting oneself in a professional manner at all times. This includes maintaining a positive attitude, being courteous and respectful towards customers, and adhering to company policies and standards.
- Problem-solving skills: Having the ability to effectively identify, analyze, and resolve customer issues or complaints. This involves being proactive in finding solutions, taking ownership of problems, and following through to ensure customer satisfaction.
By embodying these qualities, businesses can enhance their customer service experience, build customer loyalty, and establish a positive reputation in the marketplace.
FAQs
What is an RF flip chip package substrate?
An RF flip chip package substrate is a specialized component used in semiconductor packaging for high-frequency RF applications. It serves as a platform to mount integrated circuits (ICs) using flip chip technology, which enhances performance in terms of signal integrity and high-frequency operation.
What are the advantages of using RF flip chip package substrates?
RF flip chip package substrates offer advantages such as shorter signal paths, reduced parasitic capacitance and inductance, improved thermal dissipation, and higher reliability compared to traditional wire bonding methods. These benefits are crucial for maintaining signal integrity and maximizing performance in RF circuits.
What materials are used in RF flip chip package substrates?
RF flip chip package substrates are typically made from high-frequency laminates (e.g., PTFE-based materials like Rogers RO4000 series) or ceramic substrates (e.g., alumina or aluminum nitride). These materials are chosen for their low dielectric constant, low loss tangent, and excellent thermal properties, which are essential for RF applications.
How are RF flip chip package substrates manufactured?
The manufacturing process involves several steps including material selection, layer preparation, lamination (for multilayer substrates), drilling for vias and through-holes, copper deposition, circuit patterning via photolithography and etching, surface finishing (e.g., immersion gold), and quality control testing. Advanced manufacturing techniques ensure precise alignment, controlled impedance, and reliability.
What are the key considerations in designing RF flip chip package substrates?
Design considerations include selecting appropriate substrate materials, optimizing layer stackup for controlled impedance, routing RF signal traces to minimize signal loss and interference, implementing effective grounding strategies, and ensuring thermal management for heat dissipation. Designers also focus on meeting specific RF performance requirements and compatibility with flip chip ICs.
What industries use RF flip chip package substrates?
RF flip chip package substrates are used in various industries including telecommunications, aerospace, defense, automotive (e.g., radar systems), consumer electronics (e.g., smartphones), and medical devices. Any application requiring high-speed data transmission, wireless communication, or precise RF signal processing can benefit from these substrates.
 FCBGA Package Substrate manufacturer
FCBGA Package Substrate manufacturer
