Ceramics Substrate Manufacturer
Ceramics Substrate Manufacturer,Ceramics substrates are the backbone of modern electronic devices, providing a sturdy foundation for a wide range of components and circuits. Composed of advanced ceramic materials such as alumina, 窒化アルミニウム, and silicon carbide, these substrates offer exceptional thermal conductivity, 電気絶縁性, そして機械安定性. Their ability to dissipate heat efficiently makes them ideal for applications requiring high power and reliability, such as power electronics and automotive systems. Ceramics substrates are manufactured through precise processes including shaping, 発射, and surface treatment, ensuring uniformity and quality in every piece. Customizable to meet specific requirements, they come in various sizes, shapes, and thicknesses, accommodating diverse electronic designs. With their durability, environmental friendliness, and versatility, ceramics substrates play a vital role in powering the innovations of today’s technology-driven world.
What is a Ceramics Substrate?
A ceramics substrate is a base material typically made of ceramic compounds that are used in various electronic and semiconductor applications. These substrates are engineered to provide a stable and reliable foundation for electronic components, 集積回路など (ICの), 抵抗器, コンデンサー, およびその他の電子機器.
Ceramics substrates offer several advantages over other materials like plastics or metals. They possess excellent thermal conductivity, これは、電子部品から発生する熱を放散するのに役立ちます, thus ensuring the reliability and longevity of the devices. かつ, ceramics substrates exhibit good electrical insulation properties, which are crucial for preventing electrical interference and ensuring proper functioning of electronic circuits.
These substrates come in different forms, including sheets, boards, and packages, and can be customized to meet specific requirements such as size, 形, and thermal properties. They are widely used in industries such as telecommunications, 自動車, 航宇, and consumer electronics for applications ranging from power electronics to microelectronics.
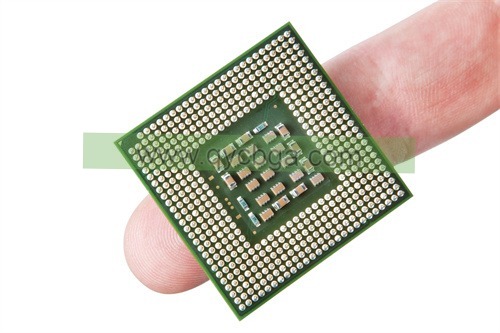
Ceramics Substrate Manufacturer
What are Ceramics Substrate Design Guidelines?
の設計ガイドライン ceramics substrates are crucial to ensure the optimal performance and reliability of electronic components and circuits. Here are some common ceramics substrate design guidelines:
- 材料の選択: Choose a ceramic material with appropriate properties for the application, such as thermal conductivity, 熱膨張係数 (CTEの), 誘電率, 機械的強度, とコスト. Common ceramics used include alumina (Al2O3), 窒化アルミニウム (AlNの), and silicon carbide (SiC).
- 寸法安定性: Ensure that the substrate material exhibits minimal dimensional changes over a range of operating temperatures to prevent stress on attached components.
- サーマルマネジメント: Design the substrate to efficiently dissipate heat generated by electronic components. This includes optimizing the substrate thickness, サーマルビア, and heat sink attachment points.
- Electrical Insulation: Maintain adequate electrical insulation between conductive traces and components to prevent short circuits. This involves proper selection of dielectric materials and careful design of insulation layers.
- シグナルインテグリティ: Minimize signal loss and electromagnetic interference (EMIの) by optimizing trace layout, インピーダンス整合, and signal routing techniques.
- 機械的安定性: Ensure the substrate can withstand mechanical stresses encountered during assembly, handling, and operation without compromising its structural integrity.
- Component Mounting: Design mounting features such as pads, ビア, and holes to facilitate the attachment of electronic components through soldering, ワイヤボンディング, またはフリップチップボンディング.
- 製造可能性: Consider manufacturability aspects such as substrate fabrication techniques (例えば。, thick-film, thin-film, or co-fired processes), tolerances, and scalability to ensure cost-effective production.
- 環境への配慮: Account for environmental factors such as humidity, temperature extremes, and exposure to chemicals or contaminants that may affect the substrate’s performance over time.
- テストと品質保証: Implement testing protocols to verify the substrate’s electrical, 熱の, および機械的特性, as well as reliability testing to ensure long-term performance under anticipated operating conditions.
これらの設計ガイドラインに従うことにより、, engineers can develop ceramics substrates that meet the specific requirements of their electronic applications while ensuring reliability, パフォーマンス, そして費用対効果.
How do you manufacture a Ceramics Substrate?
Manufacturing ceramics substrates typically involves several steps, 材料の準備を含む, 形成, 発射, and post-processing. ここでは、製造プロセスの概要をご紹介します:
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate ceramic material based on the desired properties such as thermal conductivity, 誘電率, と機械的強度. Common ceramic materials used for substrates include alumina (Al2O3), 窒化アルミニウム (AlNの), and silicon carbide (SiC).
- 材料の準備: The selected ceramic material is initially in the form of powder. It undergoes various processing steps such as milling, mixing, and shaping to achieve the desired consistency and composition. Additives may be included to enhance properties like sinterability and electrical insulation.
- 形成: The prepared ceramic material is shaped into the desired form of the substrate. This can be achieved through various techniques such as pressing (uniaxial or isostatic), 射出成形, or tape casting. Pressing involves compressing the ceramic powder into a mold under high pressure, while injection molding utilizes a heated ceramic slurry injected into a mold cavity. Tape casting involves casting a ceramic slurry onto a flat surface to form thin sheets.
- 乾燥: After shaping, the green ceramic substrates undergo a drying process to remove excess moisture. Care must be taken during drying to prevent cracking or warping of the substrates.
- 発射 (焼結): The dried green substrates are then fired in a kiln at high temperatures typically ranging from several hundred to over a thousand degrees Celsius. This process, known as sintering, causes the ceramic particles to bond together and form a dense, solid structure. The firing temperature and duration are carefully controlled to achieve the desired densification and mechanical properties.
- 表面処理: 焼結後, the substrates may undergo surface treatments such as polishing, grinding, or metallization to prepare them for subsequent processing steps or to improve surface flatness and conductivity.
- メタライゼーション: Metallization involves depositing conductive metal layers onto the substrate surface to create circuit traces, パッド, とビア. This can be accomplished through techniques such as screen printing, スパッタリング, or thick-film deposition.
- Post-Processing: Additional post-processing steps may be performed depending on the specific application requirements. This could include laser cutting, 錬成, or coating with protective or insulating materials.
- 品質管理: 製造プロセス全体を通じて, quality control measures are implemented to ensure the substrates meet the required specifications for dimensional accuracy, 表面仕上げ, 電気的特性, と信頼性.
By following these manufacturing steps and quality control measures, ceramics substrates can be produced with the necessary properties to meet the demands of various electronic applications.
How much should a Ceramics Substrate cost?
The cost of ceramics substrates can vary widely depending on several factors, including the type of ceramic material used, the substrate size and thickness, 製造プロセス, 設計の複雑さ, and desired properties such as thermal conductivity and electrical insulation.
一般的に, ceramics substrates tend to be more expensive than substrates made from other materials like FR-4 (a common epoxy-based laminate) due to the specialized manufacturing processes involved and the properties offered by ceramic materials such as high thermal conductivity and excellent electrical insulation.
As a rough estimate, the cost of ceramics substrates can range from a few dollars for simple, small-sized substrates to several hundred dollars or more for larger, custom-designed substrates with specific properties and complex features.
To get an accurate cost estimate for a ceramics substrate for a particular application, it’s best to consult with manufacturers or suppliers who can provide quotes based on the specific requirements and quantities needed. かつ, factors such as economies of scale, 注文量, and negotiation may also impact the final cost.
What is Ceramics Substrate base material?
The base material of ceramics substrates is typically a ceramic compound. The choice of ceramic material depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as thermal conductivity, 電気絶縁性, 機械的強度, とコスト. Some common ceramic materials used for substrates include:
- アルミナ (Al2O3): Alumina is one of the most widely used ceramic materials for substrates. It offers excellent mechanical strength, 熱伝導率, および電気絶縁特性. Alumina substrates are often used in high-power applications and harsh environments due to their durability and resistance to temperature extremes and corrosion.
- 窒化アルミニウム (AlNの):Aluminum nitride exhibits high thermal conductivity, making it ideal for applications requiring efficient heat dissipation, such as power electronics and high-frequency circuits. AlN substrates also offer good electrical insulation and dimensional stability.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): Silicon carbide substrates have exceptional thermal conductivity, 機械的強度, and resistance to high temperatures and harsh chemicals. SiC substrates are commonly used in high-power and high-frequency applications, as well as in environments with extreme conditions such as aerospace and automotive.
- 酸化ベリリウム (BeO(ビーオ)): Beryllium oxide offers very high thermal conductivity, second only to diamond among ceramics. しかし, due to health and safety concerns associated with beryllium exposure, its use is restricted in many applications.
These ceramic materials provide a stable and reliable foundation for electronic components and circuits, 熱のバランスを提供, 電気的な, and mechanical properties tailored to specific application requirements. Depending on the application, ceramics substrates may also incorporate additional layers or coatings to enhance performance or facilitate specific functions such as metallization for creating conductive traces.
Which company makes Ceramics Substrates?
Many companies produce ceramic substrates, including well-known names such as Kyocera, Murata, NGK, Coorstek, その他. These companies are highly reputed in the electronics, 半導体, and other industries, offering various types and specifications of ceramic substrates to meet the needs of different applications.
As for our company, we also manufacture ceramic substrates. We have advanced production equipment and technology, along with an experienced engineering team capable of designing and producing customized ceramic substrates according to customer requirements.
The production process of ceramic substrates in our company covers multiple stages, 材料の準備を含む, 形成, 焼結, 表面処理, と品質管理. We use high-quality ceramic materials such as alumina, 窒化アルミニウム, or silicon carbide, selecting the appropriate materials and processes based on customer specifications.
Throughout the production process, we maintain strict quality control to ensure that the ceramic substrates meet customer specifications and standards. Our production team possesses extensive experience and expertise, capable of meeting the requirements of various complex applications.
In addition to standard specifications, we also offer customization services, designing and manufacturing ceramic substrates according to specific customer requirements. Whether it’s material selection, size customization, 表面処理, or special requirements, we can provide professional advice and solutions.
まとめ, our company has the technological strength and professional capabilities required for ceramic substrate production, enabling us to deliver high-quality, customized products and services to customers.
は何ですか 7 優れたカスタマーサービスの品質?
優れた顧客サービスは、顧客との強固な関係を築き、顧客の満足を確保するために不可欠です. Here are seven qualities that characterize good customer service:
- 応答: 優れたカスタマーサービスには、お客様からの問い合わせに迅速に対応することが含まれます, 懸念, とリクエスト. Responding to customer needs in a timely manner shows that you value their time and are committed to helping them resolve issues quickly.
- 共感: 共感とは、他人の気持ちを理解し、共有する能力です. Good customer service representatives empathize with customers’ situations, listen attentively to their concerns, and demonstrate genuine concern for their well-being.
- Clarity: Clear communication is key to providing good customer service. Customer service representatives should convey information in a concise and understandable manner, avoiding jargon or technical language that may confuse customers.
- 知識能力: Good customer service requires having a thorough understanding of the products or services offered, as well as company policies and procedures. Customer service representatives should be knowledgeable enough to answer customer questions accurately and provide relevant information or assistance.
- プロ 意識: Professionalism encompasses behaviors such as politeness, respectfulness, そして前向きな姿勢を保つ, 困難な状況でも. カスタマーサービス担当者は、常にプロフェッショナルに振る舞う必要があります, treating customers with courtesy and professionalism.
- 柔軟性: Good customer service involves being flexible and adaptable to meet the diverse needs of customers. This may include accommodating special requests, offering alternative solutions, or adjusting policies when necessary to ensure customer satisfaction.
- Follow-up: Following up with customers after resolving their issues or inquiries demonstrates a commitment to customer satisfaction and helps to ensure that their needs have been met. Good customer service representatives follow up with customers to ensure they are satisfied with the resolution and to address any further concerns or feedback.
これらの資質を具現化することで、, businesses can deliver exceptional customer service experiences that foster loyalty, build trust, and enhance their reputation.
よくあるご質問(FAQ)
What are ceramics substrates used for?
Ceramics substrates are used as the base material for electronic components and circuits. They provide a stable foundation for mounting and interconnecting various electronic devices, 集積回路など, 抵抗器, コンデンサー, and sensors.
What types of ceramic materials are used for substrates?
Common ceramic materials used for substrates include alumina (Al2O3), 窒化アルミニウム (AlNの), silicon carbide (SiC), and beryllium oxide (BeO(ビーオ)). Each material offers different properties suited to specific applications, such as thermal conductivity, 電気絶縁性, と機械的強度.
What are the advantages of ceramics substrates?
Ceramics substrates offer several advantages, 高い熱伝導率を含む, 優れた電気絶縁性, 機械的安定性, and resistance to temperature extremes and harsh environments. These properties make ceramics substrates well-suited for use in demanding electronic applications.
How are ceramics substrates manufactured?
Ceramics substrates are typically manufactured through processes such as shaping, drying, 発射 (焼結), 表面処理, と品質管理. The specific manufacturing methods may vary depending on the type of ceramic material used and the desired substrate properties.
What factors should be considered when selecting ceramics substrates?
When selecting ceramics substrates, factors to consider include the material composition, 熱伝導率, 誘電率, 機械的強度, 寸法安定性, とコスト. The choice of substrate should be based on the specific requirements of the application.
Can ceramics substrates be customized?
はい, ceramics substrates can be customized to meet the specific requirements of different applications. Customization options may include substrate size, 形, 厚さ, 表面仕上げ, and metallization patterns, とりわけ.
Are ceramics substrates environmentally friendly?
Ceramics substrates are generally considered to be environmentally friendly materials, as they are durable, non-toxic, and chemically inert. しかし, certain ceramic materials may require special handling or disposal procedures due to their composition or manufacturing processes.
 FCBGAパッケージ基板メーカー
FCBGAパッケージ基板メーカー
