Wire Bonding Substrates Manufacturer
Wire Bonding Substrates Manufacturer,Wire bonding substrates are crucial components in microelectronics, facilitating the interconnection between semiconductor devices and external circuitry. These substrates typically feature thin films of conductive materials, such as gold or aluminum, used to bond the semiconductor chip to the substrate and connect it to external leads or contacts. They ensure reliable electrical connections while optimizing signal transmission efficiency. Wire bonding substrates are designed with precise alignment and spacing to accommodate fine-pitch bonding wires, ensuring high-density integration and compact form factors in electronic devices. They are essential in applications ranging from integrated circuits to sensors, supporting the functionality and performance of modern electronics.
What are Wire Bonding Substrates?
Wire bonding substrates refer to materials used in semiconductor and microelectronic packaging that facilitate the attachment and interconnection of integrated circuit (IC) chips to the substrate or to other components. These substrates are essential in providing a stable base for mounting and connecting IC chips within electronic devices.
Typically, wire bonding substrates are made from materials such as ceramics (like alumina or aluminum nitride), organic materials (such as FR4 or polyimide), or even metals (like copper). The choice of substrate material depends on factors like thermal management requirements, electrical properties, mechanical stability, and cost considerations.
The main function of wire bonding substrates is to provide a platform where IC chips can be securely mounted and interconnected using fine wires (usually made of gold or aluminum). This process ensures electrical connections between the chip and the rest of the circuitry, enabling the device to function as intended.
In addition to providing mechanical support and electrical connectivity, wire bonding substrates also play a crucial role in dissipating heat generated by the IC chips during operation. Efficient thermal management is essential for maintaining the reliability and longevity of electronic devices, especially those with high power densities.
Overall, wire bonding substrates are fundamental components in the assembly of semiconductor devices, contributing significantly to their performance, reliability, and overall functionality in various applications ranging from consumer electronics to aerospace and medical devices.
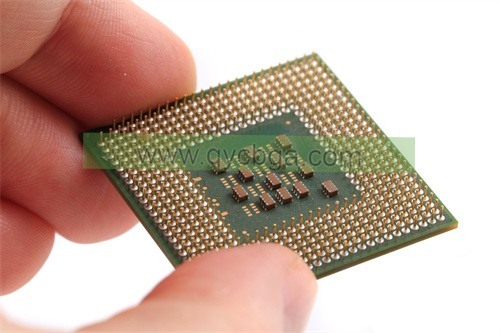
Wire Bonding Substrates Manufacturer
What are Wire Bonding Substrates Design Guidelines?
Designing wire bonding substrates involves several guidelines to ensure the reliability and functionality of the semiconductor packages. Here are some key design guidelines for wire bonding substrates:
- Material Selection: Choose substrate materials based on thermal conductivity, coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), electrical properties, and mechanical strength. Common materials include ceramics (like alumina or aluminum nitride) for high thermal conductivity or organic materials (such as FR4 or polyimide) for flexibility.
- Substrate Size and Shape: The substrate dimensions should accommodate the size of the IC chip and provide adequate space for wire bonding and routing of interconnections. The shape should facilitate easy assembly and integration into the final package.
- Pad Layout: Design the pad layout to match the bonding configuration of the IC chip. Ensure proper spacing between bonding pads to prevent shorts and facilitate wire bonding accuracy.
- Signal Integrity: Minimize signal interference and noise by careful routing of signal traces on the substrate. Maintain controlled impedance for high-speed signal paths to prevent signal degradation.
- Thermal Management: Incorporate thermal vias and heat spreaders to enhance heat dissipation from the IC chip. Ensure good thermal contact between the chip and the substrate to prevent overheating and ensure long-term reliability.
- Die Attach Area: Provide sufficient area and appropriate material for die attachment (bonding the IC chip to the substrate) to ensure strong mechanical bonding and efficient heat transfer.
- Wire Bonding Guidelines: Follow manufacturer specifications for wire bonding parameters such as wire diameter, bonding force, and bonding tooling design. Optimize bonding conditions for reliable electrical connections.
- Alignment and Registration: Ensure accurate alignment and registration features on the substrate to facilitate precise assembly of the IC chip and other components. This helps in maintaining consistency and reliability during manufacturing.
- Package Integration:Consider the overall package design and assembly process when designing the substrate. Ensure compatibility with other package components and assembly methods.
- Reliability Testing:Conduct reliability tests to validate the substrate design under operating conditions, including thermal cycling, mechanical stress, and electrical performance. Address any design weaknesses identified during testing.
By following these guidelines, designers can optimize wire bonding substrate designs to meet performance requirements, ensure manufacturing feasibility, and enhance the reliability of semiconductor packages in various applications.
What is the Wire Bonding Substrates Fabrication Process?
The fabrication process of wire bonding substrates involves several precise steps to ensure the creation of a reliable and functional base for semiconductor devices. Here is an overview of the key stages in the fabrication process:
- Material Preparation: The process begins with selecting the appropriate substrate material, typically ceramics (such as alumina or aluminum nitride) or organic materials (such as FR4 or polyimide). These materials are chosen based on their thermal, electrical, and mechanical properties.
- Substrate Cleaning: The selected substrate material undergoes thorough cleaning to remove any contaminants that could affect the subsequent processes. Cleaning methods include ultrasonic cleaning, chemical cleaning, and plasma cleaning.
- Surface Treatment: To enhance adhesion properties, the substrate surface is treated. This may involve mechanical roughening, chemical etching, or applying adhesion promoters to prepare the surface for subsequent layers.
- Patterning and Masking: A photoresist layer is applied to the substrate, followed by a photolithographic process where the desired circuit pattern is defined using a mask and UV light exposure. The exposed photoresist is developed to reveal the pattern on the substrate.
- Metallization: Metallization involves depositing a thin layer of metal, such as copper, gold, or aluminum, onto the substrate. Common deposition techniques include sputtering, evaporation, and electroplating. The metal layer forms the conductive paths and bonding pads for the IC chips.
- Etching: The unneeded metal areas are removed using chemical or plasma etching, leaving only the desired circuit pattern. This step is crucial for defining the precise conductive paths and bonding pads on the substrate.
- Dielectric Layer Application: A dielectric layer, such as polyimide or silicon dioxide, is applied over the patterned substrate to insulate different circuit layers and prevent short circuits. This layer is patterned and etched to expose the bonding pads.
- Via Formation: Vias, or vertical interconnects, are created to connect different circuit layers. This involves drilling holes through the dielectric layer and filling them with conductive material, often using plating techniques.
- Final Cleaning and Inspection: After completing the circuit pattern and vias, the substrate undergoes final cleaning to remove any residues. The substrate is then inspected for defects, ensuring it meets the required specifications for further processing.
- Die Attachment and Wire Bonding: The IC chip is attached to the prepared substrate using die attach materials, typically epoxy or solder. Wire bonding is then performed to create electrical connections between the IC chip and the bonding pads on the substrate using fine wires made of gold, aluminum, or copper.
- Encapsulation and Final Testing: The assembled substrate with the bonded IC chip is encapsulated to protect it from environmental factors. This is followed by rigorous testing to ensure the substrate meets all functional and reliability standards.
By following these steps, manufacturers can fabricate wire bonding substrates that provide a robust and reliable foundation for semiconductor devices, ensuring optimal performance in various applications.
How do you manufacture Wire Bonding Substrates?
Manufacturing wire bonding substrates involves a meticulous process to create a foundation that supports the reliable operation of semiconductor devices. Here’s an expanded overview of the manufacturing process:
- Material Selection and Preparation: The manufacturing process begins with selecting the appropriate substrate material based on the application requirements. Common materials include ceramics (such as alumina or aluminum nitride) for their excellent thermal conductivity and mechanical strength, or organic materials (like FR4 or polyimide) for their flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Once chosen, the substrates undergo rigorous cleaning to remove contaminants that could affect subsequent processing steps.
- Substrate Preparation: The cleaned substrates are inspected for defects and then prepared for the subsequent layers. This preparation may involve surface treatment methods such as mechanical roughening, chemical etching, or the application of adhesion promoters to enhance bonding between layers.
- Circuit Patterning: A critical step in substrate manufacturing is defining the circuit pattern. This is typically done using photolithography techniques where a photoresist layer is applied to the substrate surface. A mask containing the desired circuit pattern is then aligned and exposed to UV light, which transfers the pattern onto the photoresist. After exposure, the substrate undergoes a development process where the unexposed photoresist is dissolved, revealing the pattern on the substrate.
- Metallization: Once the circuit pattern is defined, metallization processes are employed to deposit conductive metals onto the substrate surface. Commonly used metals include copper, aluminum, or gold, deposited using techniques such as sputtering, evaporation, or electroplating. This metallization step creates the conductive paths (traces) and bonding pads required for interconnecting the IC chips and other components.
- Etching: Following metallization, the substrate undergoes etching processes to remove excess metal and define the precise conductive paths and bonding pad geometries. Etching can be done chemically or using plasma, ensuring the circuit pattern is accurately reproduced according to design specifications.
- Dielectric Layer Deposition: To insulate the conductive paths and protect against shorts, a dielectric layer is deposited over the metallized substrate. Dielectric materials like polyimide or silicon dioxide are applied and patterned using similar photolithography and etching techniques as the metallization process.
- Via Formation: Vias are essential for creating vertical interconnections between different layers of the substrate. Vias are typically formed by drilling holes through the dielectric layer and filling them with conductive material such as copper or other suitable metals using electroplating or similar techniques. This step ensures electrical continuity between different circuit layers.
- Surface Finishing and Cleaning: After completing the circuit pattern and vias, the substrate undergoes surface finishing processes to improve solderability and prevent oxidation. Final cleaning steps are crucial to remove any residues or contaminants that could affect the reliability of the substrate during operation.
- Assembly and Bonding: Once prepared, the substrates are ready for assembly with IC chips and other components. Die attach materials, such as epoxy adhesives or solder, are used to bond the IC chips onto the substrate. Wire bonding techniques are then employed to create electrical connections between the IC chips and the bonding pads on the substrate. Fine wires made of gold, aluminum, or copper are precisely bonded using ultrasonic or thermosonic bonding methods.
- Encapsulation and Testing: The assembled substrates with bonded IC chips may undergo encapsulation to protect them from environmental factors like moisture and mechanical stress. Finally, rigorous testing procedures are performed to ensure the substrates meet all functional and reliability specifications. Testing may include electrical testing for continuity and performance under various conditions, thermal cycling tests to assess reliability, and visual inspections to detect any defects.
By following these comprehensive manufacturing steps, manufacturers can produce high-quality wire bonding substrates that provide a robust foundation for semiconductor devices, ensuring reliable performance in diverse applications from consumer electronics to automotive and aerospace industries.
How much should Wire Bonding Substrates cost?
The cost of wire bonding substrates can vary significantly depending on several factors including material choice, substrate size, complexity of design, manufacturing processes involved, and volume of production. Here are some key considerations that influence the cost:
- Material:The type of material used for the substrate plays a crucial role. Ceramics like alumina or aluminum nitride are generally more expensive than organic materials such as FR4 or polyimide. Specialty materials with enhanced thermal or electrical properties can also increase costs.
- Manufacturing Processes:The complexity and number of manufacturing processes involved in producing the substrates affect the cost. Processes such as photolithography, metallization, etching, via formation, and dielectric deposition require specialized equipment and skilled labor, contributing to overall costs.
- Size and Complexity: Larger substrates or those with complex circuit patterns and multiple layers typically incur higher costs due to increased material usage, longer processing times, and higher precision requirements.
- Volume of Production: Economies of scale apply in substrate manufacturing. Higher volumes generally reduce per-unit costs due to efficiencies in material procurement, batch processing, and equipment utilization.
- Quality and Specifications: Substrates manufactured to tighter tolerances, higher reliability standards, or with specific customization requirements (such as unique materials or advanced features) may command higher prices.
- Additional Features: Certain substrates may include additional features such as embedded components, specialized coatings, or enhanced thermal management solutions, which can increase costs.
To provide a rough estimate, basic wire bonding substrates used in standard semiconductor packaging applications can range from a few dollars per piece for simpler designs in larger quantities, to tens or even hundreds of dollars per piece for high-performance substrates with advanced materials and features, especially in low-volume or specialized applications.
Ultimately, the cost of wire bonding substrates is influenced by a combination of material selection, manufacturing complexity, customization needs, and volume considerations. Manufacturers and designers often work closely to balance these factors while meeting performance and budgetary requirements for their specific applications.
What is Wire Bonding Substrates base material?
The base material used for wire bonding substrates varies depending on the specific application requirements, but typically includes a variety of materials chosen for their thermal, mechanical, and electrical properties. Here are some common base materials used in wire bonding substrates:
- Ceramics:
– Alumina (Al2O3): Known for its high thermal conductivity, alumina substrates are commonly used in applications where heat dissipation is critical. Alumina substrates are also mechanically strong and have good dielectric properties.
– Aluminum Nitride (AlN): Aluminum nitride substrates offer even higher thermal conductivity than alumina, making them suitable for high-power applications where efficient heat dissipation is essential.
- Organic Materials:
– FR4 (Flame Retardant 4): FR4 is a type of epoxy-based laminate used widely in PCB (Printed Circuit Board) manufacturing. It is cost-effective, mechanically robust, and suitable for many electronic applications.
– Polyimide: Polyimide substrates offer flexibility, excellent thermal stability, and resistance to chemicals and radiation. They are used in flexible electronics and applications requiring high temperature resistance.
- Metals:
– Copper: Copper substrates are less common but are used in specialized applications where high electrical conductivity and thermal dissipation are required.
– Aluminum: Aluminum substrates are lightweight and have moderate thermal conductivity, suitable for certain electronic packaging applications.
- Composite Materials:
– Ceramic-filled Polymers: These materials combine the mechanical strength of ceramics with the flexibility of polymers. They are used in applications requiring a balance of properties such as strength, thermal management, and electrical insulation.
The choice of base material for wire bonding substrates depends on factors such as thermal management requirements, electrical insulation, mechanical strength, cost considerations, and specific application needs. Designers and manufacturers select the most appropriate material to ensure optimal performance and reliability of semiconductor devices in various operating conditions.
Which company makes Wire Bonding Substrates?
Many companies specialize in manufacturing and supplying wire bonding substrates for semiconductor and microelectronic packaging. Some well-known companies include Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd., Toray Industries, Inc., Nikon Corporation from Japan, as well as Corning Incorporated, Texas Instruments Incorporated, and others from the United States. These companies provide various types of wire bonding substrates globally, catering to different industries and applications.
At our company, we also have the capability to manufacture and supply high-quality wire bonding substrates. As a dedicated player in the semiconductor and microelectronics industry, we possess advanced manufacturing facilities and a skilled technical team, enabling us to offer the following advantages and capabilities:
- Material Selection and Process Control: We can select suitable substrate materials such as ceramics (e.g., alumina, aluminum nitride) or organic materials (e.g., FR4, polyimide) based on customer requirements and ensure their quality and performance through precise process control.
- Customized Design and Manufacturing: We can customize designs and manufacturing processes according to customer specifications, including complex circuit patterns, multi-layer structures, and specialized thermal management solutions.
- Quality Control and Certification: We adhere to international quality management standards such as ISO 9001 to ensure our products meet customer quality requirements. Our production includes rigorous testing and inspection to ensure reliability and consistency of each batch.
- Responsive and Flexible Production Capacity: We have the capability to respond quickly to customer needs and complete the entire production cycle from design to delivery in a short timeframe. Our production facilities are flexible to accommodate orders of different scales and types.
- Technical Support and Service: With a professional technical team, we provide technical support and solutions to help customers optimize designs and resolve technical issues during production.
In summary, our company not only has the capability to manufacture wire bonding substrates but also strives to provide high-quality, customized solutions to customers. With excellent technical support and service, we aim to collaborate with customers to drive innovation and advancement in the semiconductor and microelectronics industry.
What are the 7 qualities of good customer service?
Good customer service is characterized by several key qualities that contribute to positive customer experiences and satisfaction. Here are seven essential qualities:
- Responsiveness: Customers appreciate prompt responses to their inquiries, whether through phone calls, emails, or in-person interactions. Timely assistance demonstrates respect for their time and urgency.
- Empathy: Effective customer service involves understanding and empathizing with the customer’s situation. It requires listening actively, acknowledging their concerns, and showing genuine empathy towards their feelings and experiences.
- Clarity: Providing clear and concise information is crucial. Customers should receive accurate details about products, services, policies, and any other relevant information. Clear communication helps prevent misunderstandings and builds trust.
- Patience: Dealing with customer inquiries or issues may require patience, especially in complex or challenging situations. Patient service representatives remain calm, listen attentively, and work towards resolving issues without rushing the customer.
- Professionalism: Maintaining a professional demeanor and attitude is essential. This includes being courteous, respectful, and maintaining a positive tone even in difficult interactions. Professionalism builds credibility and trust with customers.
- Problem-solving skills: Effective customer service involves the ability to analyze problems, identify solutions, and take proactive steps to resolve issues. Service representatives should be resourceful and capable of offering practical solutions to meet customer needs.
- Follow-up: Following up with customers after resolving their issues or inquiries shows commitment and care. It ensures that customers are satisfied with the outcome and provides an opportunity to address any further concerns they may have.
By embodying these qualities, organizations can deliver exceptional customer service that enhances customer loyalty, fosters positive word-of-mouth, and contributes to overall business success.
FAQs
What are wire bonding substrates?
Wire bonding substrates are materials used in semiconductor and microelectronic packaging to mount and interconnect integrated circuit (IC) chips. They provide a stable base for wire bonding connections and facilitate electrical pathways between the IC chips and other components.
What materials are commonly used for wire bonding substrates?
Common materials include ceramics (such as alumina or aluminum nitride) known for their thermal conductivity and mechanical strength, as well as organic materials like FR4 or polyimide which offer flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
What are the key factors to consider when choosing wire bonding substrates?
Factors include thermal conductivity, electrical properties, mechanical strength, cost, and compatibility with manufacturing processes. The choice depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as heat dissipation and signal integrity.
How are wire bonding substrates manufactured?
The manufacturing process typically involves material selection, cleaning, surface preparation, circuit patterning using photolithography, metallization, etching, dielectric layer deposition, via formation, and final assembly with IC chips and wire bonding.
What types of wire bonding are used with these substrates?
Wire bonding techniques include ball bonding and wedge bonding. Ball bonding uses a fine wire where a ball is formed at one end, while wedge bonding uses a wedge-shaped tool to create a direct bond between the wire and the bonding pad.
What are the advantages of wire bonding substrates?
Wire bonding substrates provide efficient electrical connectivity, good thermal management, mechanical stability, and reliability in semiconductor packaging. They support miniaturization and integration of electronic components in various applications.
What are some applications of wire bonding substrates?
They are used in diverse industries such as consumer electronics, automotive electronics, telecommunications, medical devices, and aerospace. Applications include microprocessors, sensors, memory devices, and integrated circuits.
How can I ensure the reliability of wire bonding substrates in my application?
Reliability can be ensured through rigorous testing, adherence to industry standards, proper material selection, and quality manufacturing processes. Testing methods include thermal cycling, mechanical stress tests, and electrical performance evaluations.

