Military PCB Manufacturer
Military PCB Manufacturer,Military PCBs are specialized circuit boards designed and manufactured to meet the rigorous demands of military applications. Engineered with utmost precision and using high-quality materials, Military PCBs excel in reliability, durability, and performance under extreme conditions. These PCBs are built to withstand harsh environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations, moisture, vibration, and electromagnetic interference, ensuring consistent operation in mission-critical situations. Incorporating advanced design techniques, robust construction, and stringent quality control measures, Military PCBs offer unmatched resilience and longevity in defense systems, communication equipment, radar systems, avionics, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). With adherence to strict military standards and certifications, Military PCBs uphold the highest levels of quality, ensuring the integrity and effectiveness of military operations in even the most challenging environments.
What is a Military PCB?
A Military PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is a circuit board specifically designed and manufactured for use in military applications. These PCBs are built to withstand harsh environmental conditions, extreme temperatures, shock, vibration, and other challenges typically encountered in military operations.
Key features of military PCBs may include:
- Durability:They are constructed using high-quality materials and fabrication processes to ensure robustness and longevity.
- Reliability: Military PCBs must function reliably in critical situations, so they undergo rigorous testing and adhere to strict quality standards.
- Temperature and Environmental Resistance: They are engineered to operate within wide temperature ranges and resist moisture, humidity, dust, and other environmental factors.
- EMI/RFI Shielding: Military PCBs often incorporate shielding techniques to protect against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI).
- High Performance: These PCBs are designed to meet the demanding performance requirements of military equipment, including high-speed data transmission and signal integrity.
- Compliance: They may need to adhere to specific military standards and certifications, such as MIL-STD-810 for environmental testing or MIL-PRF-31032 for manufacturing requirements.
Military PCBs are used in various military applications, including communication systems, radar systems, weapons platforms, avionics, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), among others. They play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and functionality of military equipment in challenging and often hostile environments.
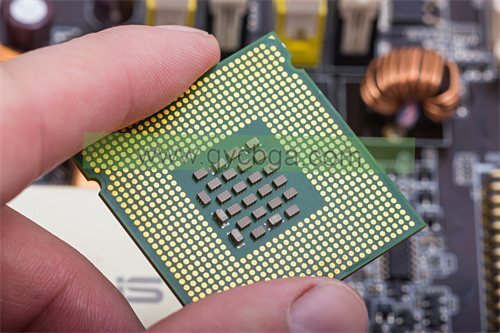
Military PCB Manufacturer
What are the Military PCB Design Guidelines?
Military PCB design guidelines focus on creating circuit boards that meet the stringent requirements of military applications, ensuring reliability, durability, and performance in harsh environments. Here are some key guidelines typically followed in military PCB design:
- Reliability: Reliability is paramount in military applications. PCB designs should prioritize robustness and long-term performance under extreme conditions.
- Environmental Considerations: Military PCBs must withstand a wide range of environmental factors, including temperature extremes, humidity, vibration, shock, and exposure to chemicals. Designers should select materials and components that can endure these conditions.
- Size and Weight Constraints: Military equipment often has strict size and weight limitations. PCB designs should aim for compactness and efficiency without compromising functionality or durability.
- Signal Integrity:High-speed data transmission is common in military applications. Designers must carefully manage signal integrity to minimize noise, crosstalk, and signal degradation, often through controlled impedance routing and proper ground and power plane design.
- EMI/RFI Shielding: Military PCBs must resist electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) to maintain operational integrity. Shielding techniques such as grounded metal enclosures, shielding layers, and careful component placement can help mitigate interference.
- Component Selection:Military-grade components with extended temperature ranges, high reliability ratings, and long-term availability should be preferred. Commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) components may be acceptable if they meet stringent military standards.
- Power Management: Efficient power management is crucial for military systems to maximize battery life and ensure reliable operation. PCB designs should minimize power consumption and incorporate features such as power gating and voltage regulation.
- Testing and Verification: Extensive testing and verification are essential to ensure that military PCBs meet performance and reliability requirements. Designers should conduct thorough design reviews, simulations, and prototype testing, as well as comply with relevant military standards and certifications.
- Compliance with Military Standards: Military PCB designs must often adhere to specific standards and regulations, such as MIL-STD-810 for environmental testing, MIL-PRF-31032 for manufacturing requirements, and others depending on the application.
By adhering to these guidelines, designers can create military PCBs that meet the stringent requirements of military applications, ensuring reliability, durability, and performance in challenging environments.
What is the Military PCB Fabrication Process?
The fabrication process for military PCBs involves several steps to ensure that the resulting circuit boards meet the stringent requirements of military applications. Here is an overview of the typical military PCB fabrication process:
- Design Preparation: The process begins with the preparation of the PCB design using specialized PCB design software. Designers lay out the circuitry, components, and routing according to the specifications and requirements of the military application. They may also incorporate design features to enhance reliability, durability, and performance.
- Material Selection: Military PCBs require materials that can withstand harsh environmental conditions and provide high reliability. Designers select materials such as high-quality laminate substrates, copper foils, and solder mask materials that meet military standards for temperature range, flame resistance, chemical resistance, and other properties.
- Manufacturing Documentation: Detailed manufacturing documentation, including Gerber files, drill files, and assembly drawings, is prepared to guide the fabrication process and ensure consistency between the design and the final product.
- Panelization: PCB designs are often combined into panels to optimize fabrication efficiency. Panels may contain multiple PCBs arranged in a grid, with routing and breakaway tabs between individual boards.
- Lamination: The lamination process involves bonding together multiple layers of substrate material, copper foil, and prepreg (a resin-coated fiberglass material) to form the layered structure of the PCB. The layers are sandwiched together and subjected to heat and pressure to create a solid laminate.
- Drilling: Precision CNC drilling machines are used to drill holes in the PCB for through-hole components, vias, and mounting holes. The drill files generated from the PCB design guide the drilling process to ensure accuracy and alignment.
- Through-Hole Plating: After drilling, the holes in the PCB are plated with copper to create electrical connections between layers. This process, known as through-hole plating or electroplating, involves depositing a thin layer of copper inside the holes using an electrochemical process.
- Circuit Patterning: A photoresist layer is applied to the surface of the PCB and exposed to ultraviolet light through a photomask, which contains the circuit pattern. The exposed areas of the photoresist harden, while the unexposed areas remain soluble. The PCB is then developed to remove the unexposed photoresist, leaving behind the circuit pattern.
- Etching: The PCB is immersed in an etchant solution, typically containing chemicals such as ferric chloride, which selectively removes the exposed copper from the PCB surface, leaving only the desired copper traces and pads.
- Surface Finishing: Surface finishing processes, such as immersion gold, electroless nickel immersion gold (ENIG), or tin-lead plating, are applied to the exposed copper surfaces to improve solderability, corrosion resistance, and wire bonding capabilities.
- Solder Mask Application: A solder mask layer is applied to the surface of the PCB to protect the copper traces and pads from environmental contaminants and prevent solder bridges during assembly. The solder mask is selectively applied using a screen printing or liquid photoimageable (LPI) process.
- Silkscreen Printing: Component designators, polarity markings, logos, and other identifying information are printed onto the PCB surface using a silkscreen printing process. This information helps assembly technicians identify components and ensure proper orientation during assembly.
- Testing and Inspection: After fabrication, PCBs undergo rigorous testing and inspection to verify functionality, electrical continuity, and adherence to specifications. Testing may include automated optical inspection (AOI), electrical testing (e.g., continuity testing, impedance testing), and dimensional inspection.
- Quality Assurance: Military PCB fabrication facilities adhere to strict quality assurance procedures to ensure that all PCBs meet the required standards and specifications. Quality control measures are implemented throughout the fabrication process to detect and rectify any defects or deviations from the requirements.
- Packaging and Shipping: Once PCBs pass inspection, they are packaged according to customer requirements and shipped to the assembly facility for component placement and soldering.
By following these steps and adhering to strict quality standards, military PCB fabrication facilities produce circuit boards that meet the reliability, durability, and performance requirements of military applications.
How do you manufacture a Military PCB?
Manufacturing a military PCB involves several steps, each critical to ensuring the final product meets the stringent requirements of military applications. Here’s an overview of the typical manufacturing process:
- Design Preparation: The process begins with the creation or receipt of the PCB design files. These files contain the layout of the circuitry, components, and routing, as well as any specific design features required for military applications. Design preparation may also involve compliance checks with military standards and regulations.
- Material Selection: Military PCBs require high-quality materials that can withstand harsh environmental conditions and provide long-term reliability. Manufacturers select materials such as high-grade laminate substrates, copper foils, solder mask materials, and surface finishes that meet military specifications for temperature range, flame resistance, chemical resistance, and other properties.
- Panelization: PCB designs are often combined into panels to optimize manufacturing efficiency. Panels may contain multiple PCBs arranged in a grid, with routing and breakaway tabs between individual boards.
- Lamination: The lamination process involves bonding together multiple layers of substrate material, copper foil, and prepreg (resin-coated fiberglass material) to create the layered structure of the PCB. The layers are stacked and laminated under heat and pressure to form a solid laminate.
- Drilling: Precision CNC drilling machines are used to drill holes in the PCB for through-hole components, vias, and mounting holes. The drill files generated from the PCB design guide the drilling process to ensure accuracy and alignment.
- Through-Hole Plating: After drilling, the holes in the PCB are plated with copper to create electrical connections between layers. This process, known as through-hole plating or electroplating, involves depositing a thin layer of copper inside the holes using an electrochemical process.
- Circuit Patterning: A photoresist layer is applied to the surface of the PCB and exposed to ultraviolet light through a photomask, which contains the circuit pattern. The exposed areas of the photoresist harden, while the unexposed areas remain soluble. The PCB is then developed to remove the unexposed photoresist, leaving behind the circuit pattern.
- Etching: The PCB is immersed in an etchant solution, typically containing chemicals such as ferric chloride, which selectively removes the exposed copper from the PCB surface, leaving only the desired copper traces and pads.
- Surface Finishing: Surface finishing processes, such as immersion gold, electroless nickel immersion gold (ENIG), or tin-lead plating, are applied to the exposed copper surfaces to improve solderability, corrosion resistance, and wire bonding capabilities.
- Solder Mask Application: A solder mask layer is applied to the surface of the PCB to protect the copper traces and pads from environmental contaminants and prevent solder bridges during assembly. The solder mask is selectively applied using a screen printing or liquid photoimageable (LPI) process.
- Silkscreen Printing: Component designators, polarity markings, logos, and other identifying information are printed onto the PCB surface using a silkscreen printing process. This information helps assembly technicians identify components and ensure proper orientation during assembly.
- Testing and Inspection: After manufacturing, PCBs undergo rigorous testing and inspection to verify functionality, electrical continuity, and adherence to specifications. Testing may include automated optical inspection (AOI), electrical testing (e.g., continuity testing, impedance testing), and dimensional inspection.
- Quality Assurance: Military PCB manufacturers adhere to strict quality assurance procedures to ensure that all PCBs meet the required standards and specifications. Quality control measures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process to detect and rectify any defects or deviations from the requirements.
- Packaging and Shipping: Once PCBs pass inspection, they are packaged according to customer requirements and shipped to the assembly facility for component placement and soldering.
By following these steps and adhering to strict quality standards, military PCB manufacturers produce circuit boards that meet the reliability, durability, and performance requirements of military applications.
How much should a Military PCB cost?
The cost of a military PCB can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the complexity of the design, the materials used, the manufacturing processes involved, the quantity ordered, and any specific requirements or certifications needed for military applications. Here are some factors that can influence the cost of a military PCB:
- Complexity of Design: PCBs with intricate layouts, high component density, and advanced features such as high-speed signaling or impedance control may require more time and resources to manufacture, resulting in higher costs.
- Materials: Military-grade materials that meet stringent requirements for reliability, durability, and performance often come at a premium compared to standard materials. Specialized laminates, copper foils, solder masks, and surface finishes designed for military applications can contribute to higher costs.
- Manufacturing Processes: Certain manufacturing processes, such as high-precision drilling, advanced surface finishing techniques, and stringent quality control measures, may incur additional costs. Military PCBs may also require specialized equipment and expertise to meet the demanding requirements of military standards and certifications.
- Quantity Ordered: The economies of scale typically apply to PCB manufacturing, meaning that larger order quantities often result in lower unit costs. However, military PCBs are often produced in smaller volumes due to the specialized nature of military applications, which can lead to higher per-unit costs compared to mass-produced consumer electronics PCBs.
- Certifications and Compliance: Military PCBs may need to comply with specific military standards and certifications, such as MIL-PRF-31032 for manufacturing requirements or MIL-STD-810 for environmental testing. Achieving and maintaining these certifications can involve additional costs, including testing, documentation, and ongoing quality assurance efforts.
- Customization and Prototyping: Customized designs, prototype iterations, and engineering support services can add to the overall cost of military PCB manufacturing, particularly if additional time and resources are required to refine the design or address specific customer requirements.
- Supply Chain and Market Conditions: Fluctuations in raw material prices, availability of components, and market demand can impact the cost of military PCBs. Factors such as geopolitical events, global economic conditions, and supply chain disruptions may influence pricing dynamics.
Given these factors, it’s challenging to provide a specific cost range for military PCBs without knowing the specific requirements of the project. Military PCBs are generally more expensive than commercial-grade PCBs due to the additional requirements for reliability, durability, and performance, as well as the specialized materials and processes involved. It’s advisable for organizations seeking military PCBs to work closely with reputable manufacturers or suppliers to obtain accurate cost estimates based on their unique requirements and specifications.
What is Military PCB base material?
The base material for military PCBs, like those used in other high-reliability applications, plays a critical role in ensuring the durability, reliability, and performance of the circuit board in harsh environmental conditions. Here are some common materials used as the base substrate for military PCBs:
- FR-4 (Flame Retardant 4): FR-4 is one of the most widely used substrates for PCBs in general, including military applications. It consists of woven fiberglass cloth impregnated with an epoxy resin binder. FR-4 offers good mechanical strength, electrical insulation properties, and dimensional stability. It is also flame retardant, which is important for safety in military environments.
- Polyimide (PI): Polyimide is a high-performance polymer known for its excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. PCBs made with polyimide substrates can withstand extreme temperatures and harsh environments, making them suitable for military applications in aerospace, defense, and other industries.
- PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene): PTFE-based substrates, such as Teflon, offer exceptional dielectric properties, low loss tangent, and high thermal stability. PCBs made with PTFE substrates are often used in military radar systems, communication equipment, and other high-frequency applications where signal integrity and performance are critical.
- Rogers Corporation Materials: Rogers Corporation manufactures a range of high-performance substrates specifically designed for demanding applications, including military and aerospace. Materials such as RO4000 series and RO3000 series offer excellent electrical properties, thermal stability, and reliability for high-frequency and high-speed PCB designs.
- Metal Core Substrates: For military applications that require enhanced thermal management or resistance to electromagnetic interference (EMI), metal core substrates may be used. These substrates typically consist of a metal core, such as aluminum or copper, sandwiched between layers of dielectric material. Metal core substrates provide superior heat dissipation and EMI shielding capabilities compared to traditional FR-4 substrates.
- Ceramic Substrates: In certain military applications where extreme temperature, vibration, and reliability are paramount, ceramic substrates may be used. Ceramic materials offer excellent thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and stability under harsh conditions. PCBs made with ceramic substrates are commonly found in military avionics, missile guidance systems, and other mission-critical equipment.
The choice of base material for military PCBs depends on factors such as the specific requirements of the application, environmental conditions, performance criteria, and budget constraints. Designers and manufacturers of military PCBs carefully select the appropriate substrate material to ensure that the resulting circuit boards meet the demanding requirements of military applications for reliability, durability, and performance.
Which company makes Military PCBs?
Many companies produce military PCBs, and some of them specialize in providing high-reliability, high-performance circuit board solutions for the military sector. Manufacturers worldwide offer military PCBs, and some well-known companies include Northrop Grumman, Raytheon, Lockheed Martin, BAE Systems, among others. These companies possess extensive experience and expertise to design and manufacture PCBs that comply with stringent military standards for various military applications such as communication systems, radar systems, aircraft controls, navigation systems, and more.
As for our company, we also manufacture military PCBs. We have advanced manufacturing equipment, a professional engineering team, and rich experience to meet the strict requirements of military applications. Our manufacturing processes comply with international standards, including the ISO 9001 Quality Management System and industry standards such as IPC-A-600, IPC-A-610, and others. We can provide various types of military PCBs, including multilayer boards, rigid-flex boards, high-frequency boards, etc., to meet the needs of different military applications. Our PCBs feature excellent electrical performance, stable characteristics, and high reliability, enabling them to operate stably for extended periods in extreme environments. Our team can also provide customized solutions based on specific customer requirements to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
As a professional PCB manufacturer, we are committed to providing high-quality products and excellent services to our customers. We will continue to invest in technological innovation and quality control to meet the evolving market demands and customer expectations. If you are interested in our military PCB solutions, please feel free to contact us, and we will be happy to provide support and cooperation.
What are the qualities of good customer service?
Good customer service is characterized by several qualities that contribute to a positive and satisfying experience for customers. Here are some key qualities:
- Effective Communication: Good customer service begins with effective communication. Representatives should listen actively to customers, understand their needs and concerns, and provide clear and helpful responses.
- Empathy:Empathy involves understanding and acknowledging the customer’s feelings, perspectives, and situations. Empathetic customer service representatives show genuine concern for the customer’s well-being and strive to address their needs with compassion and understanding.
- Patience: Dealing with customer inquiries, complaints, or issues often requires patience, especially when customers are frustrated or upset. Patient representatives remain calm, composed, and attentive, even in challenging situations, and work diligently to resolve issues to the customer’s satisfaction.
- Product Knowledge: Good customer service requires a thorough understanding of the products or services offered. Representatives should be knowledgeable about product features, specifications, usage instructions, and troubleshooting procedures to provide accurate information and assistance to customers.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Customer service representatives should possess strong problem-solving skills to address customer issues effectively. They should be proactive in identifying and resolving problems, exploring alternative solutions, and taking appropriate action to ensure customer satisfaction.
- Flexibility: Flexibility is essential in adapting to diverse customer needs and preferences. Representatives should be adaptable and willing to accommodate customer requests, whether it’s modifying an order, adjusting a service plan, or finding creative solutions to meet unique requirements.
- Professionalism: Professionalism encompasses behaviors such as courtesy, respect, integrity, and reliability. Customer service representatives should maintain a professional demeanor at all times, communicate politely and respectfully, and uphold ethical standards in their interactions with customers.
- Timeliness: Responding to customer inquiries or resolving issues in a timely manner is crucial for providing good customer service. Representatives should strive to address customer needs promptly, whether it’s answering questions, processing orders, or following up on concerns.
- Follow-Up: Good customer service doesn’t end with the initial interaction; it also involves follow-up to ensure customer satisfaction and resolution. Representatives should follow up with customers after resolving an issue or completing a transaction to ensure that their needs have been met and to gather feedback for improvement.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Ultimately, good customer service is centered around the needs and preferences of the customer. Representatives should prioritize customer satisfaction, anticipate their needs, and go above and beyond to exceed their expectations whenever possible.
By embodying these qualities, organizations can cultivate a culture of excellent customer service and build strong relationships with their customers, leading to increased loyalty, positive word-of-mouth, and long-term success.
FAQs
What are Military PCBs?
Military PCBs are printed circuit boards specifically designed and manufactured for use in military applications. These PCBs are built to withstand harsh environmental conditions, extreme temperatures, shock, vibration, and other challenges typically encountered in military operations.
What are the key features of Military PCBs?
Key features of Military PCBs include durability, reliability, temperature and environmental resistance, EMI/RFI shielding, high performance, compliance with military standards, and suitability for various military applications such as communication systems, radar systems, avionics, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
What materials are used in the fabrication of Military PCBs?
Military PCBs use high-quality materials such as specialized laminate substrates, copper foils, solder mask materials, and surface finishes that meet military standards for temperature range, flame resistance, chemical resistance, and other properties.
What are the design guidelines for Military PCBs?
Design guidelines for Military PCBs focus on creating circuit boards that meet the stringent requirements of military applications. These guidelines include considerations for reliability, environmental resistance, signal integrity, EMI/RFI shielding, component selection, testing and verification, compliance with military standards, and more.
How are Military PCBs manufactured?
The manufacturing process for Military PCBs involves several steps, including design preparation, material selection, panelization, lamination, drilling, through-hole plating, circuit patterning, etching, surface finishing, solder mask application, silkscreen printing, testing and inspection, quality assurance, and packaging and shipping.
What factors influence the cost of Military PCBs?
The cost of Military PCBs can vary depending on factors such as the complexity of the design, materials used, manufacturing processes involved, quantity ordered, certifications and compliance requirements, customization, and market conditions.
What companies manufacture Military PCBs?
Several companies specialize in the design and manufacture of Military PCBs, including well-known defense contractors such as Northrop Grumman, Raytheon, Lockheed Martin, BAE Systems, and others, as well as specialized PCB manufacturers with expertise in military applications.
What are the benefits of using Military PCBs?
The benefits of using Military PCBs include high reliability, durability, performance, environmental resistance, compliance with military standards, suitability for mission-critical applications, and long-term operational stability in harsh conditions.

