Advanced BT BGA PCB Manufacturer
Advanced BT BGA PCB Manufacturer.Advanced BT BGA PCBs are sophisticated printed circuit boards tailored for cutting-edge Bluetooth applications. Integrating Ball Grid Array (BGA) components, they offer superior performance in high-speed data transfer, power efficiency, and wireless connectivity. These PCBs are meticulously designed with RF optimization, precise antenna placement, and robust signal integrity. Manufactured with high-quality materials and advanced techniques, they ensure reliability and durability in diverse electronic devices such as smartphones, IoT devices, wearables, and automotive electronics. Advanced BT BGA PCBs represent the pinnacle of technology, enabling seamless and efficient Bluetooth communication in the modern digital era.
What is an Advanced BT BGA PCB?
An Advanced BT BGA PCB refers to a printed circuit board (PCB) designed to accommodate Ball Grid Array (BGA) components, specifically tailored for advanced Bluetooth (BT) applications. BGA is a packaging technology that mounts the device onto the surface of the PCB using an array of small solder balls instead of pins, offering advantages like increased density and improved electrical performance.
In the context of Bluetooth technology, an Advanced BT BGA PCB would likely incorporate features optimized for high-speed data transfer, low power consumption, and robust wireless connectivity. This could include specialized RF (radio frequency) design, signal integrity considerations, and integration with other components such as antennas and power management circuitry.
Moreover, the “advanced” designation suggests that this PCB may support the latest Bluetooth standards, such as Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) or Bluetooth 5, offering enhanced features like longer range, higher data throughput, and improved security.
Designing an Advanced BT BGA PCB requires expertise in PCB layout, RF engineering, and Bluetooth protocols to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Additionally, adherence to industry standards and best practices is essential to meet the requirements of modern Bluetooth-enabled devices, such as smartphones, IoT devices, wearables, and automotive electronics.
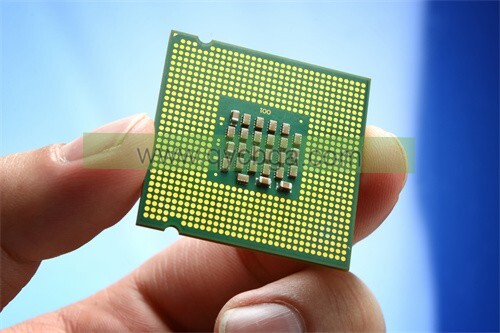
Advanced BT BGA PCB Manufacturer
What are the Advanced BT BGA PCB Design Guidelines?
Designing an Advanced BT (Bluetooth) BGA (Ball Grid Array) PCB requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Here are some guidelines:
- RF Considerations: Pay close attention to RF (Radio Frequency) design principles. Proper RF layout techniques, such as impedance matching, signal isolation, and controlled impedance traces, are crucial for maintaining signal integrity and minimizing interference.
- Antenna Placement: Ensure that the PCB layout accommodates the placement of the Bluetooth antenna(s) in optimal locations for maximum signal strength and coverage. Avoid placing antennas near metal components or other RF-sensitive areas that could cause signal blockage or interference.
- Power Integrity: Implement power distribution networks (PDNs) that minimize voltage drops and noise, especially in areas critical for RF performance. Proper decoupling capacitor placement and power plane design are essential for maintaining stable power supply to the BGA components.
- Thermal Management: BGA components can generate significant heat, especially during high-speed data transfer. Incorporate thermal vias, heatsinks, and proper PCB layer stackup to dissipate heat efficiently and prevent overheating that could degrade performance or damage components.
- Signal Integrity: Ensure signal integrity by minimizing signal reflections, crosstalk, and electromagnetic interference (EMI). Use techniques such as controlled impedance routing, signal shielding, and proper ground plane design to maintain signal integrity throughout the PCB.
- Manufacturability: Consider manufacturability during PCB layout to ensure that the design can be reliably manufactured and assembled. Pay attention to BGA pad layout, solder mask openings, and assembly tolerances to prevent soldering defects and ensure proper BGA attachment.
- Compliance with Standards: Ensure that the PCB design complies with relevant industry standards and regulations, including Bluetooth SIG (Special Interest Group) requirements. Compliance testing may be necessary to certify the Bluetooth functionality and interoperability of the final product.
- Testability: Design the PCB with test points and access for debugging and testing during development and production. Incorporate built-in self-test (BIST) features where possible to facilitate diagnostic testing and troubleshooting.
By following these guidelines, designers can create Advanced BT BGA PCBs that meet the stringent requirements of modern Bluetooth applications, ensuring high performance, reliability, and compliance with industry standards.
What is the Advanced BT BGA PCB Fabrication Process?
The fabrication process for an Advanced BT (Bluetooth) BGA (Ball Grid Array) PCB involves several steps to transform the design into a physical circuit board ready for assembly. Here’s an overview of the typical process:
- Design Preparation: The fabrication process begins with the preparation of the PCB design files. This includes the PCB layout, which specifies the placement of components, routing of traces, and other design elements. Design files are typically generated using PCB design software and saved in formats compatible with PCB fabrication equipment.
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate PCB substrate material based on the requirements of the design, such as dielectric constant, thermal conductivity, and cost. Common substrate materials for BGA PCBs include FR-4 (flame retardant 4), which is a widely used epoxy-based laminate, and specialized materials optimized for RF applications.
- Preparation of Substrate: The selected substrate material is prepared by cutting it to the desired size and cleaning the surface to remove any contaminants that could affect the adhesion of copper and other layers.
- Copper Cladding: Copper foil is laminated onto the substrate to create the conductive layers of the PCB. The copper foil is bonded to the substrate using heat and pressure, and excess foil is trimmed to size.
- Photoresist Application: A layer of photoresist material is applied to the surface of the copper foil. Photoresist is a light-sensitive material that will be used to create the PCB’s circuit pattern.
- Exposure and Development: The PCB design pattern is transferred onto the photoresist layer using a process called photolithography. UV light is passed through a photomask containing the circuit pattern, exposing the photoresist in the desired areas. The exposed photoresist is then developed to remove the unexposed areas, revealing the underlying copper.
- Etching: The exposed copper is etched away using chemical solutions, leaving behind the desired circuit traces on the PCB. Etching is typically performed using acidic solutions that dissolve the copper but do not affect the substrate material.
- Drilling: Holes are drilled into the PCB to accommodate through-hole components and vias. High-precision drilling equipment is used to create holes with diameters as small as a fraction of a millimeter.
- Surface Finish: The exposed copper surfaces are coated with a surface finish to protect them from oxidation and facilitate soldering during assembly. Common surface finishes for BGA PCBs include HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), and OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative).
- Quality Control: The fabricated PCB undergoes inspection and testing to ensure that it meets the required specifications for dimensions, tolerances, and electrical continuity. Automated optical inspection (AOI) and electrical testing are commonly used to detect defects and verify the functionality of the PCB.
Once the fabrication process is complete, the Advanced BT BGA PCB is ready for assembly, where BGA components and other surface-mount devices are soldered onto the board to create the final electronic product.
How do you manufacture an Advanced BT BGA PCB?
Manufacturing an Advanced BT (Bluetooth) BGA (Ball Grid Array) PCB involves a series of steps from design validation to final assembly. Here’s a detailed outline of the manufacturing process:
- Design Validation: Before manufacturing begins, it’s crucial to validate the PCB design to ensure it meets the requirements for Bluetooth functionality, signal integrity, and manufacturability. This may involve simulation, prototyping, and testing to verify the design’s performance.
- Material Procurement: Once the design is validated, the necessary materials are procured. This includes the PCB substrate material (e.g., FR-4), copper foil for conductive layers, solder mask, silkscreen ink, and surface finish chemicals.
- Preparation of Substrate: The selected substrate material is prepared by cutting it to the desired size and cleaning the surface to remove any contaminants. The substrate may also undergo surface treatment processes to enhance adhesion and facilitate subsequent manufacturing steps.
- Copper Cladding: Copper foil is laminated onto the substrate to form the conductive layers of the PCB. The copper foil is bonded to the substrate using heat and pressure, and excess foil is trimmed to size.
- Drilling:Holes are drilled into the PCB to accommodate through-hole components and vias. High-precision drilling equipment is used to create holes with diameters as small as needed for the BGA components.
- Inner Layer Imaging:A photoresist layer is applied to the surface of the copper foil on inner layers. The PCB design pattern is then transferred onto the photoresist layer using photolithography techniques. After exposure and development, the unwanted copper is etched away, leaving behind the desired circuit traces.
- Layer Alignment and Bonding: Multiple layers of the PCB are aligned and bonded together to form the multilayer stack. Alignment is critical to ensure that the vias and traces on different layers line up correctly.
- Outer Layer Imaging: Similar to inner layer imaging, a photoresist layer is applied to the surface of the outer copper layers. The PCB design pattern is transferred onto the photoresist layer using photolithography, and the unwanted copper is etched away.
- Surface Finish Application:The exposed copper surfaces are coated with a surface finish to protect them from oxidation and facilitate soldering during assembly. Common surface finishes for BGA PCBs include HASL, ENIG, and OSP.
- Solder Mask Application: A solder mask layer is applied to the PCB to insulate the copper traces and prevent solder bridges during assembly. Openings are created in the solder mask layer to expose the pad areas for soldering.
- Silkscreen Printing: Information such as component outlines, reference designators, and logos are printed onto the PCB using silkscreen ink for assembly and identification purposes.
- Quality Control: The manufactured PCBs undergo thorough inspection and testing to ensure they meet the required specifications for dimensions, tolerances, and electrical continuity. Automated optical inspection (AOI) and electrical testing are commonly used to detect defects.
Once the PCBs pass quality control, they are ready for assembly, where BGA components and other surface-mount devices are soldered onto the board to create the final electronic product. Advanced BT BGA PCB manufacturing requires precision, attention to detail, and adherence to industry standards to ensure the reliability and performance of the finished product.
How much should an Advanced BT BGA PCB cost?
The cost of an Advanced BT (Bluetooth) BGA (Ball Grid Array) PCB can vary widely depending on factors such as complexity, size, quantity, material specifications, and manufacturing processes. However, I can provide a rough estimate based on typical industry standards and considerations.
- Complexity: The complexity of the PCB design, including the number of layers, density of components, and routing requirements, significantly impacts the cost. More complex designs with intricate routing and high component density generally cost more to manufacture.
- Size: Larger PCBs require more material and processing time, resulting in higher costs. Conversely, smaller PCBs may be more cost-effective to manufacture.
- Material Specifications: The choice of materials, such as substrate type, copper thickness, and surface finish, can affect the cost. Specialized materials optimized for RF performance or high-speed data transfer may be more expensive than standard materials.
- Manufacturing Processes: Advanced manufacturing processes, such as high-precision drilling, controlled impedance routing, and specialized surface finishes, can increase the cost of PCB production.
- Quantity: Economies of scale typically apply in PCB manufacturing, meaning that larger production quantities often result in lower per-unit costs. However, prototype or small-batch production runs may incur higher costs per unit.
- Supplier and Location: PCB manufacturing costs can vary depending on the chosen supplier and their location. Suppliers with advanced capabilities and state-of-the-art equipment may charge higher prices for their services.
As a rough estimate, the cost of manufacturing an Advanced BT BGA PCB could range from a few dollars for a simple, low-complexity design in small quantities to several hundred dollars or more for a highly complex design with specialized materials and processes in larger quantities.
For a more accurate cost estimate, it’s advisable to consult with PCB manufacturers or suppliers and provide detailed specifications of the desired PCB design, including quantity, materials, and manufacturing requirements. They can provide quotes based on your specific needs and production volume.
What is the Advanced BT BGA PCB base material?
The choice of base material for an Advanced BT (Bluetooth) BGA (Ball Grid Array) PCB depends on various factors such as performance requirements, cost considerations, and manufacturing constraints. However, a common and widely used base material for such applications is FR-4 (Flame Retardant 4).
FR-4 is a widely used epoxy-based laminate that offers several advantages suitable for Advanced BT BGA PCBs:
- Electrical Performance: FR-4 provides good electrical insulation properties, low dielectric constant, and stable electrical performance over a wide range of frequencies. This is important for maintaining signal integrity and minimizing interference in high-frequency applications such as Bluetooth.
- Mechanical Strength: FR-4 is known for its mechanical strength and dimensional stability, making it suitable for applications where the PCB may be subjected to mechanical stress or environmental factors.
- Thermal Properties: FR-4 has adequate thermal conductivity properties to dissipate heat generated by BGA components, although additional thermal management techniques may be required for advanced designs with high power dissipation.
- Cost-Effectiveness: FR-4 is relatively inexpensive compared to other specialized materials, making it a cost-effective choice for many applications.
While FR-4 is commonly used, there are also specialized materials available for specific requirements in Advanced BT BGA PCBs. For example, some applications may benefit from high-frequency laminate materials optimized for RF performance or materials with enhanced thermal conductivity for improved heat dissipation.
Ultimately, the choice of base material should be based on the specific requirements of the application, including performance, cost, and manufacturability considerations. Consulting with PCB designers and manufacturers can help determine the most suitable base material for a particular Advanced BT BGA PCB design.
Which company manufactures Advanced BT BGA PCBs?
Many companies are capable of manufacturing Advanced BT BGA PCBs, including large electronics manufacturing enterprises, specialized PCB manufacturers, and custom electronic design and manufacturing service providers. Some well-known companies may include Foxconn, EU PCB, Feida Electronics, and others. These companies typically possess advanced production equipment, extensive experience, and professional teams capable of meeting various complex PCB manufacturing needs.
Our company is also a professional PCB manufacturer with the technology and resources required to produce Advanced BT BGA PCBs. Here are some advantages and capabilities of our company in manufacturing Advanced BT BGA PCBs:
- Technical Strength: We have advanced PCB manufacturing technology and equipment, including high-precision PCB production lines, automated process control systems, and more. Our technical team has rich experience and expertise to provide customized solutions for complex design requirements.
- Quality Assurance: We strictly adhere to the ISO quality management system and employ rigorous quality control processes to ensure that every PCB meets customer specifications and industry standards. We have comprehensive quality inspection equipment and processes to ensure stable and reliable product quality.
- Flexible Production Capacity:Our production capacity is flexible and diverse, capable of meeting orders of different scales and requirements. Whether it’s small batch customization or large-scale mass production, we can deliver high-quality products promptly.
- Customer Customization Services: We emphasize communication and cooperation with customers to provide customized solutions based on their requirements. Our sales and technical teams will provide full-service support to ensure that customer needs are met throughout the process.
In summary, our company possesses the technology, resources, and experience required to manufacture Advanced BT BGA PCBs and can provide high-quality, reliable products and services. We are willing to collaborate with customers to drive development in the electronics manufacturing industry.
What are the 7 qualities of good customer service?
Good customer service is characterized by several key qualities that contribute to positive interactions and relationships with customers. Here are seven qualities of good customer service:
- Responsiveness: Good customer service involves promptly addressing customer inquiries, concerns, and requests. Responding to customers in a timely manner demonstrates attentiveness and a commitment to meeting their needs efficiently.
- Empathy: Empathy is essential in understanding and acknowledging the emotions and perspectives of customers. Showing empathy towards customers’ frustrations or challenges helps build rapport and fosters trust in the service provider.
- Clarity: Effective communication is crucial in providing good customer service. Clear and concise communication helps ensure that customers understand the information provided and can make informed decisions. Avoiding jargon and using simple language contributes to clarity in communication.
- Professionalism: Professionalism involves maintaining a courteous and respectful demeanor when interacting with customers. Treating customers with professionalism regardless of the situation reinforces the company’s commitment to customer satisfaction.
- Problem-solving skills: Good customer service representatives possess strong problem-solving skills to address customer issues and resolve conflicts effectively. Being proactive in finding solutions demonstrates a commitment to resolving issues and meeting customer expectations.
- Consistency: Consistency in service delivery is key to building customer loyalty and trust. Providing consistently high-quality service across all interactions and channels reinforces the company’s reputation and fosters long-term relationships with customers.
- Personalization: Tailoring the customer experience to individual preferences and needs demonstrates a customer-centric approach to service delivery. Personalization can involve remembering customer preferences, anticipating their needs, and offering relevant recommendations or solutions.
By embodying these qualities, businesses can cultivate a culture of excellent customer service and create positive experiences that lead to customer satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is an Advanced BT BGA PCB?
An Advanced BT BGA PCB is a printed circuit board designed to accommodate Ball Grid Array (BGA) components specifically tailored for advanced Bluetooth applications. It incorporates features optimized for high-speed data transfer, low power consumption, and robust wireless connectivity.
What are the advantages of using BGA components in BT PCBs?
BGA components offer advantages such as increased density, improved electrical performance, and better thermal characteristics compared to traditional packaging methods. They are well-suited for compact and high-performance Bluetooth applications.
What are the key design considerations for Advanced BT BGA PCBs?
Design considerations include RF (radio frequency) performance, antenna placement, power integrity, thermal management, signal integrity, manufacturability, compliance with standards, and testability.
What materials are commonly used for Advanced BT BGA PCBs?
Common base materials include FR-4 (Flame Retardant 4), which offers good electrical performance, mechanical strength, and cost-effectiveness. Specialized materials optimized for RF performance or thermal conductivity may also be used for specific applications.
How are Advanced BT BGA PCBs manufactured?
The manufacturing process involves steps such as design preparation, material procurement, substrate preparation, copper cladding, drilling, imaging, etching, surface finish application, solder mask application, silkscreen printing, and quality control.
What are the typical costs associated with Advanced BT BGA PCBs?
Costs vary depending on factors such as complexity, size, quantity, material specifications, and manufacturing processes. A rough estimate ranges from a few dollars for simple designs to several hundred dollars or more for complex designs in larger quantities.
Which companies manufacture Advanced BT BGA PCBs?
Many companies, including electronics manufacturing enterprises, specialized PCB manufacturers, and custom electronic design and manufacturing service providers, are capable of manufacturing Advanced BT BGA PCBs.
What are the qualities of good customer service when sourcing Advanced BT BGA PCBs?
Good customer service qualities include responsiveness, empathy, clarity in communication, professionalism, problem-solving skills, consistency, and personalization in addressing customer inquiries and requirements.

