What is ABF(Ajinomoto) Package Substrate?
ABF(Ajinomoto) Fabricante de sustratos de paquetes,ABF (Película de acumulación Ajinomoto) package substrate is a cutting-edge material used in semiconductor packaging, known for its exceptional electrical properties and reliability. This substrate employs a build-up film technology, enabling the creation of multiple layers of conductive traces and insulating materials in a compact form factor. ABF substrates offer high thermal conductivity, excellent signal integrity, y estabilidad mecánica, making them ideal for high-speed and high-density applications. Commonly utilized in advanced semiconductor packages like FCBGA and WLP, ABF package substrates ensure reliable performance and durability in diverse electronic devices, from smartphones to data centers, where space efficiency and reliability are critical.
FCBGA stands for “Flip-Chip Ball Grid Array.” It’s a type of integrated circuit packaging technology used in the semiconductor industry. In FCBGA packaging, the silicon die (the actual integrated circuit) is flipped upside down and mounted directly onto the substrate (usually a ceramic or organic material).
The substrate contains a grid array of solder balls, which serve as the electrical connections between the die and the circuit board it’s mounted on. This type of packaging offers several advantages, including better electrical performance, improved thermal management, and a smaller footprint compared to traditional packaging methods.
The substrate itself is a key component of the FCBGA package. It provides mechanical support for the die and facilitates the electrical connections between the die and the rest of the system. The substrate material can vary depending on the specific requirements of the application, but it’s typically a high-performance material capable of handling the electrical and thermal demands of the integrated circuit.
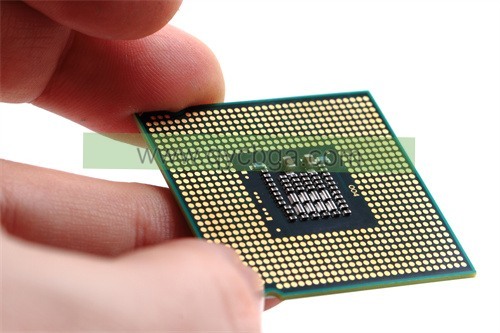
ABF(Ajinomoto) Fabricante de sustratos de paquetes
ABF(Ajinomoto) Package Substrate design Reference Guide.
The ABF (Ajinomoto Buildup Film) sustrato is a type of packaging substrate used in semiconductor manufacturing. It’s a build-up substrate made of layers of insulating material with embedded copper traces to create the electrical connections between the various components of an integrated circuit. Ajinomoto is a company known for its development and production of ABF substrates.
A reference guide for ABF package substrate design would typically include information on:
- Substrate Material Specifications: Details about the composition and properties of the ABF substrate material, including electrical, termal, and mechanical characteristics.
- Directrices de diseño: Guidelines for designing the layout of the substrate, including rules for trace routing, Vía de colocación, pad sizes, and layer stack-up.
- Consideraciones sobre la integridad de la señal: Information on minimizing signal degradation and electromagnetic interference (EMI) through proper substrate design, including controlled impedance routing and power distribution network design.
- Gestión térmica: Strategies for managing heat dissipation within the package, such as thermal vias and heat spreaders, to ensure proper functioning of the integrated circuit.
- Package Size and Dimensions: Recommendations for determining the appropriate size and dimensions of the substrate based on the specific requirements of the application.
- Reliability Guidelines: Guidelines for ensuring the long-term reliability of the package, including considerations for solder joint integrity, Tensión mecánica, y factores ambientales.
- Manufacturing and Assembly Guidelines: Recommendations for manufacturing processes, such as substrate fabrication and assembly techniques, to ensure high-yield production and quality.
- Electrical Test Guidelines: Guidelines for testing the electrical performance of the substrate, including test methodologies and criteria for acceptable performance.
These are some of the key aspects that would typically be covered in a reference guide for ABF package substrate design. It serves as a comprehensive resource for engineers and designers involved in the development of integrated circuits using ABF substrates.
What are the materials used in ABF(Ajinomoto) Package Substrate?
The ABF (Ajinomoto Buildup Film) package substrate is typically composed of several layers of materials, each serving specific functions in the construction and performance of the substrate. While exact compositions may vary depending on specific requirements and applications, here are the typical materials used in ABF package substrates:
- Buildup Layers: The core of the ABF substrate consists of multiple buildup layers, which are thin films of insulating material. These layers are typically made of a polymer material such as polyimide or epoxy resin. These layers provide electrical insulation between the copper traces and facilitate the creation of multilayer interconnect structures.
- Copper Traces: Embedded within the buildup layers are copper traces, which serve as conductive pathways for electrical signals. These traces are patterned using lithographic processes and are typically plated onto the insulating layers. Copper provides good electrical conductivity and is suitable for high-speed signal transmission.
- Barrier Layers: In some cases, barrier layers may be included within the buildup structure to prevent diffusion of copper ions into the insulating material, which could degrade its electrical properties over time. Barrier layers are typically made of materials such as titanium or tantalum.
- Solder Mask: The topmost layer of the substrate is often a solder mask, which is a protective coating applied over the copper traces to prevent oxidation and facilitate soldering during assembly. Solder mask materials are typically epoxy-based or polyimide-based and are applied using a screen printing process.
- Acabado superficial: The exposed copper pads on the substrate’s surface may be coated with a surface finish to enhance solderability and prevent oxidation. Los acabados superficiales comunes incluyen níquel químico, inmersión, oro (ENIG), organic solderability preservative (OSP), y lata de inmersión o plata.
- Adhesive Layers: Adhesive layers may be used in ABF substrates to bond the buildup layers together and to attach the substrate to other components in the package assembly. Adhesive materials are typically epoxy-based and are applied as thin films between the buildup layers during fabrication.
These are the primary materials used in the construction of ABF package substrates. The specific composition and layering scheme may vary depending on factors such as performance requirements, Procesos de fabricación, and cost considerations.
How is ABF(Ajinomoto) Package Substrate manufactured?
The manufacturing process for ABF (Película de acumulación Ajinomoto) package substrates involves several steps to create high-density interconnect (IDH) substrates suitable for semiconductor packaging. While specific details may vary depending on the manufacturer and the exact requirements of the application, the general process typically includes the following key stages:
- Preparación del sustrato: The process begins with the preparation of the base substrate material, typically a polyimide film. The film may undergo surface treatment to enhance adhesion and promote uniformity.
- Laminación: Multiple layers of dielectric material, usually in the form of dry films or liquid resins, are laminated onto the base substrate. These layers serve as the insulation between conductive traces and define the substrate’s electrical and mechanical properties.
- Patrón de circuitos: Copper foil is bonded to the dielectric layers using an adhesive, and then the desired circuit patterns are created through processes such as photolithography and etching. Photolithography involves applying a photoresist layer onto the copper foil, exposing it to UV light through a photomask with the desired circuit pattern, and then developing the resist to define the pattern. Etching removes the exposed copper, leaving behind the desired traces.
- Vía Formación: Vias, which are small holes drilled or formed through the substrate layers, are created to establish electrical connections between different layers of the substrate. This can be achieved using laser drilling, mechanical drilling, or via punching processes.
- Build-Up Process: Additional dielectric layers and conductive traces are sequentially added using a build-up process, which involves repeating the lamination, Patrones, and via formation steps as necessary to achieve the desired number of layers and interconnect density.
- Acabado superficial: The substrate’s surface is typically coated with a solder mask to define solderable areas and protect the underlying copper traces. Surface finishes such as immersion gold or electroless nickel immersion gold (ENIG) may also be applied to improve solderability and corrosion resistance.
- Final Inspection and Testing: The completed ABF package substrates undergo rigorous inspection and testing to ensure they meet quality and performance standards. This may include visual inspection, Pruebas eléctricas, and reliability testing to assess factors such as thermal cycling, solder joint reliability, and dimensional accuracy.
By following these manufacturing steps, ABF package substrate manufacturers can produce high-quality substrates tailored to the specific requirements of semiconductor packaging applications, including those demanding high-density interconnects, fine-pitch traces, and excellent electrical performance.
The Application area of ABF(Ajinomoto) Package Substrate
ABF (Película de acumulación Ajinomoto) package substrates find applications in various sectors of the semiconductor industry, particularly in advanced packaging technologies where space constraints, high signal density, and superior electrical performance are critical factors. Some common application areas include:
- Mobile Devices: ABF substrates are widely used in the packaging of mobile devices such as smartphones, Tabletas, y wearables. Their thin profile, lightweight nature, and ability to accommodate high-density interconnects make them ideal for compact and portable electronics.
- Electrónica de consumo: Beyond mobile devices, ABF substrates are also employed in a range of consumer electronics products including digital cameras, gaming consoles, smart home devices, and portable media players. These applications benefit from ABF substrates’ ability to support miniaturization and high-speed data transfer.
- Networking and Telecommunications: ABF package substrates play a crucial role in networking and telecommunications equipment such as routers, Interruptores, Estaciones base, and optical transceivers. These applications demand high-performance interconnect solutions to support data communication and networking protocols.
- Electrónica automotriz: In the automotive industry, ABF substrates are used in advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), Sistemas de infoentretenimiento, engine control units (ECU), and other electronic components. They offer reliability, thermal stability, and the ability to withstand harsh operating conditions.
- Aplicaciones Industriales: ABF substrates are also employed in various industrial applications such as industrial automation, robótica, Sistemas de control, and instrumentation. Their ability to handle high-speed data transmission and operate in demanding environments makes them well-suited for industrial applications.
- Dispositivos médicos: In the medical sector, ABF substrates are utilized in medical imaging equipment, patient monitoring devices, diagnostic tools, y dispositivos médicos implantables. They offer reliability, miniaturización, and high-density interconnects critical for medical device design.
- Aeroespacial y Defensa: ABF package substrates are used in aerospace and defense applications including avionics, Sistemas de radar, communication equipment, y sistemas de guiado de misiles. They provide the reliability, rendimiento, and ruggedness required for aerospace and defense electronics.
En general, ABF package substrates are versatile solutions that cater to a wide range of applications across industries where compact size, high performance, and reliability are paramount. Their ability to meet stringent requirements for miniaturization, high-speed data transfer, and thermal management makes them indispensable in the semiconductor packaging landscape.
What are the advantages of ABF(Ajinomoto) Package Substrate?
ABF (Película de acumulación Ajinomoto) package substrates offer several advantages that make them attractive options for semiconductor packaging applications. Algunas de las principales ventajas son:
- High-Density Interconnects: ABF substrates enable the creation of high-density interconnects, allowing for more compact and miniaturized electronic packages. This is particularly beneficial in applications where space constraints are critical, such as mobile devices and wearable electronics.
- Fine-Pitch Traces: ABF substrates support the creation of fine-pitch traces with narrow linewidths and tight spacing between conductive elements. This capability enables the integration of complex circuits and facilitates high-speed data transmission in advanced electronic systems.
- Flexible Substrate: ABF substrates are inherently flexible, allowing them to conform to curved or irregular surfaces. This flexibility makes them suitable for applications where rigid substrates are impractical or where mechanical stress must be minimized, such as in wearable devices or flexible displays.
- Excellent Electrical Performance: ABF substrates offer excellent electrical properties, including low dielectric loss, high insulation resistance, and consistent signal integrity. These properties contribute to the overall performance and reliability of electronic systems, particularly in high-frequency and high-speed applications.
- Gestión térmica: ABF substrates exhibit good thermal conductivity and heat dissipation properties, helping to manage thermal issues in electronic packages. This is essential for maintaining device reliability and preventing performance degradation due to overheating, especialmente en aplicaciones de alta potencia.
- Reliability and Durability: ABF substrates are designed to meet stringent reliability standards, ensuring long-term performance and durability in demanding operating environments. They offer resistance to mechanical stress, moisture, and thermal cycling, enhancing the reliability of electronic systems.
- Capacidad de fabricación: ABF substrates are compatible with standard manufacturing processes used in the semiconductor industry, such as photolithography, aguafuerte, and lamination. This simplifies the manufacturing process and reduces production costs, making ABF substrates a cost-effective choice for high-volume production.
- Environmental Friendliness: ABF substrates are manufactured using environmentally friendly materials and processes, making them a sustainable option for semiconductor packaging. They comply with regulations related to hazardous substances and contribute to the overall sustainability of electronic products.
En general, ABF package substrates offer a combination of performance, flexibilidad, and reliability that makes them well-suited for a wide range of semiconductor packaging applications. Their ability to meet the evolving demands of electronic systems while offering manufacturing efficiency and environmental sustainability makes them a preferred choice for many designers and manufacturers.
How Much Does ABF(Ajinomoto) Package Substrate Cost?
The cost of ABF (Película de acumulación Ajinomoto) package substrates can vary depending on several factors, including the substrate’s specifications, complejidad, quantity ordered, y las condiciones del mercado. Generalmente, ABF substrates are considered to be competitively priced compared to other advanced packaging technologies, but specific pricing information may not be readily available due to the proprietary nature of pricing agreements between manufacturers and customers.
Factors influencing the cost of ABF package substrates include:
- Costos de material: El costo de las materias primas, including polyimide film, copper foil, dielectric materials, adhesivos, and surface finishes, contributes significantly to the overall cost of ABF substrates. Prices of these materials can fluctuate based on market demand and availability.
- Manufacturing Process Complexity: The complexity of the manufacturing process required to produce ABF substrates can impact costs. More intricate designs, finer traces, higher layer counts, and additional features such as embedded components or thermal management structures may increase manufacturing costs.
- Descuentos por volumen: Manufacturers often offer volume discounts for large orders, with lower per-unit costs for higher quantities. Customers ordering in bulk may benefit from reduced prices per substrate.
- Customization and Additional Services: Customization options such as unique designs, Materiales especiales, or additional testing and certification services may incur additional costs. Customers should consider their specific requirements and budget constraints when requesting customized ABF substrates.
- Relaciones con los proveedores: Long-term relationships between customers and suppliers can sometimes lead to preferential pricing agreements or other cost-saving opportunities. Establishing strong partnerships with suppliers may result in more competitive pricing for ABF substrates.
- Market Competition: Competition among ABF substrate manufacturers can influence pricing dynamics. Customers may compare quotes from multiple suppliers to find the best combination of price, quality, and service.
Para obtener información específica sobre los precios, customers typically need to contact ABF substrate manufacturers directly to request a quote based on their project requirements and volume needs. Adicionalmente, industry analysts and market research reports may provide insights into pricing trends and competitive dynamics within the ABF substrate market.
FAQs about ABF(Ajinomoto) Package Substrate
What is ABF package substrate?
ABF package substrate is a type of high-density interconnect (IDH) substrate used in semiconductor packaging. It consists of multiple layers of dielectric material with embedded copper traces, offering advantages such as high density, excellent electrical performance, and flexibility.
What are the advantages of using ABF package substrates?
Some advantages of ABF package substrates include high-density interconnects, fine-pitch traces, flexibilidad, excellent electrical performance, thermal management capabilities, fiabilidad, and environmental friendliness.
What are the main applications of ABF package substrates?
ABF package substrates are used in various sectors of the semiconductor industry, including mobile devices, consumer electronics, networking and telecommunications, Electrónica automotriz, Aplicaciones industriales, Dispositivos médicos, and aerospace and defense.
¿Cómo se fabrican los sustratos de paquetes ABF??
The manufacturing process for ABF package substrates involves steps such as substrate preparation, lamination, Patrón de circuitos, Vía de formación, build-up process, Acabado superficial, and final inspection and testing.
What materials are used in ABF package substrates?
ABF package substrates typically consist of materials such as polyimide film, copper foil, dielectric materials (p. ej.., epoxy resins, polyimides, liquid crystal polymers), adhesive layers, barrier films, Máscara de soldadura, and surface finishes.
What factors can affect the cost of ABF package substrates?
The cost of ABF package substrates can vary depending on factors such as material costs, manufacturing process complexity, Descuentos por volumen, customization and additional services, Relaciones con los proveedores, and market competition.
Where can I find more information about ABF package substrates?
Additional information about ABF package substrates can be obtained from manufacturers, Publicaciones de la industria, technical conferences, and online resources dedicated to semiconductor packaging technologies.
 Fabricante de sustratos de paquetes FCBGA
Fabricante de sustratos de paquetes FCBGA







